Infrastructure Guidance for COVID-19/Alternate Care Sites: Difference between revisions
| Line 218: | Line 218: | ||
== Infection prevention and control == | == Infection prevention and control == | ||
General guidance for COVID-19 [[Infrastructure Guidance for COVID-19/COVID-19 Infection Prevention and Control|Infection Prevention and Control]] can be accessed [[Infrastructure Guidance for COVID-19/COVID-19 Infection Prevention and Control|here]]<br> | |||
Infection prevention and control in the context of COVID-19 should respond to transmission routes of primary concern for the pathogen of interest (contact and droplet transmission, and management of risk waste) as well as infection risk of a general nature (water and sewerage, airborne transmission – under high TB/HIV burden, and general waste). | Infection prevention and control in the context of COVID-19 should respond to transmission routes of primary concern for the pathogen of interest (contact and droplet transmission, and management of risk waste) as well as infection risk of a general nature (water and sewerage, airborne transmission – under high TB/HIV burden, and general waste). | ||
| Line 227: | Line 228: | ||
=== Standard precautions === | === Standard precautions === | ||
'''Water and sewerage contamination:''' The International Water Association | '''Water and sewerage contamination:''' The International Water Association [[Infrastructure Guidance for COVID-19/Alternate Care Sites/COVID-19 A Water Professionals Perspective|concluded]] that water and sewerage contamination is not considered to be a key risk factor for COVID-19. The panel expressed concern for “how waste and specifically wastewater (medical) would be handled by places (e.g., hostels, hotels) that are used to serve as interim COVID-19 quarantine or testing facilities or accommodation ([ACS]. These are places other than hospitals that are used in the interim for such purposes and do not usually handle wastewater from medical settings. Such facilities should be monitored carefully.”<br> | ||
'''Airborne transmission:''' Under exceptional circumstances the risk of airborne transmission arises for SARS-CoV-2, as tabulated below. | '''Airborne transmission:''' Under exceptional circumstances the risk of airborne transmission arises for SARS-CoV-2, as tabulated below. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! Why it this even in a Table | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
As SARS-CoV-2 is not considered airborne, respiratory protection against airborne transmission is not considered necessary, except where aerosolisation of particles may be a risk. | |||
According to CDC | |||
*tracheal intubation, | |||
*non-invasive ventilation, | |||
*tracheotomy, | |||
*cardiopulmonary resuscitation, or | |||
*manual ventilation before intubation and bronchoscopy. | |||
According to doctors in the field also when performing | |||
*COVID-19 diagnostic sampling as patients can be induced to cough and sneeze. | |||
*Suspected or confirmed comorbidity of TB is not an additional risk where correct COVID-19 PPE is applied. | |||
|} | |||
== Site Layout == | == Site Layout == | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 18 April 2020
Return to Infrastructure Guidance for COVID-19
Infrastructure Guidance for COVID-19/Alternate Care Sites2
Infrastructure Minimum Guidelines for Alternate Care Sites for COVID-19
This guidance work was initiated under project titled:
Reducing Nosocomial and Community-Acquired Tuberculosis by Strengthening the Capacity of the South African Department of Health to Improve Implementation of Infection Control and Waste Management at All Levels of the Health System Under the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR)
Purpose and approach
The global pandemic of COVID-19 caused by the coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 is likely to result in a surge in need for medical care for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) in South Africa. Considering the course of the pandemic in other countries, it is anticipated that South African hospitals will not have sufficient capacity to cope with the surge of persons requiring medical attention and that surge capacity via alternate care sites (ACS) will need to be established.
Surge capacity, contemplated here is not the frequent emergency department overcrowding experienced by healthcare facilities (e.g. Friday/Saturday night emergencies) or local casualty emergency that might overcrowd nearby facilities and have little to no impact on the overall healthcare delivery system. It is when a catastrophic event occurs and the affected population seek medical care from existing local healthcare facilities, causing healthcare infrastructure to become exhausted due to excess in demand. During a healthcare surge, the standard of care will shift from focusing on patient-based outcomes to population-based outcomes, and providers should anticipate “a shift to providing care and allocating scarce equipment, supplies and personnel in a way that saves the largest number of lives in contrast to the traditional focus on saving individuals.”[1]
Surge capacity can be temporarily established in non-traditional environments, such as hotels, exhibition halls, community halls, and as field hospitals, on open spaces.
In the context of this document, a quarantine site is a facility for patients who do not require continuous professional medical care, while an ACS is defined as a temporary facility that can provide continuous medical care for SARS. This document provides principles and considerations, high-level guidance for minimum requirements and examples for ACS.
While an extensive set of health facility guidelines does exist[2] , these are applicable for conventional facilities and thus include services and guidelines that are not necessarily relevant to the treatment of a novel, highly infectious pathogen, with pandemic effects. Moreover these do not provide well for the rapid and temporary establishment of facilities.
In order to formulate high-level guidance, the team reached out to professional industry bodies for inputs, in particular the South African Institute for Architects (SAIA), The Gauteng Institute for Architects (GiFA) Gauteng Institute for Architecture and the South African Federation of Hospital Engineering (SAFHE), by inviting input via a 36-hour research charrette. Relevant historical and contemporary literature was consulted, precedents identified and critically reviewed. Material from the Infrastructure Unit System Support (IUSS), international literature and guidance and input gathered from the broader architectural, engineering and healthcare professional communities was synthesised and moderated by the CSIR team. The draft was reviewed by an expert review panel. Contributors and reviewers are acknowledged in text.
Notes
Scope and Assumptions
ACSs as discussed in this document are dedicated, temporary facilities for triage, testing, diagnosis, on-referral and treatment of persons:
- suspected of having contracted SARS-CoV-2, (persons under investigation (PUIs)), who are symptomatic and/or are awaiting results,
- or are confirmed to be infected.
ACS will accommodate a variety of clinical, logistical, support and auxiliary services associated with the render of care. ACS will currently not be licensed to provide healthcare services. Since the ACS will operate in a non-healthcare facility, it cannot fully replace a hospital setting and its prime objective is to manage the patient load until the local healthcare system can meet demands.
Exclusions:
Quarantine facilities are accommodation facilities where a member of the community can remain for the duration of their isolation period. This is typically temporary housing for a cohort of people who do not need intensive medical attention but who cannot stay at home. Patients can take care of themselves and need limited monitoring by medical staff. Quarantine: Containing presumptive-case patients from each other and the general population. Quarantine facilities – that is for asymptomatic persons who are in the community in self- or imposed isolation, but not displaying symptoms, or who are symptomatic, but are able to safely recover without clinical intervention and do not need continuous medical observation are not considered in this document.
Service regime
The following assumptions are made with respect to services under consideration.
- Temporary - limited to the part of the pandemic when the “conventional” hospital platform cannot meet demand. To be dismantled, thereafter.
- Uncomplicated, dedicated COVID-19 care. Patients with comorbidities, paediatrics will be prioritised for conventional facilities.
- 24 hour, 7 days a week operations.
Assumed mechanism of transmission
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is understood to be preferentially transmitted from person to person by the contact and droplet routes with opportunistic airborne transmission and negligible water transmission risks in special Fecal-oral circumstances. Reclassification of transmission mechanisms may nullify some of the approaches presented in this guidance.
A call for strategic coordination
This document focusses on infrastructure requirements. These provisions are meaningless without staffing, equipping and resourcing. Whilst staffing, equipping and resourcing are not the focus of this document, these are likely to emerge as key constraining features. Resource constraints are likely to become acute during this pandemic. Doctors and nurses are already in critical short supply in South Africa and internationally, and are themselves susceptible to COVID-19 infection. Equipment and consumables are in short supply with heightened global demand, reduced manufacturing capacity and limits in trade flows. This necessitates strategic coordination, proactive planning, options appraisal and prioritisation.
Status quo
Rationale and transmission status
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), based on the largest cohort of COVID-19 patients, about 40% of patients with COVID-19 may have mild disease, where treatment is mostly symptomatic and does not require inpatient care. About 40% of patients have moderate disease that may require inpatient care; 15% of patients will have severe disease that requires oxygen therapy or other inpatient interventions; and about 5% have critical disease that requires the patient to receive mechanical ventilation. However, the evolution of the outbreak in some countries has shown a higher proportion of severe and critical cases and the need to rapidly increase surge capacity to prevent rapid exhaustion of biomedical supplies and staff. In some countries, doubling rates of cases every three days has been observed[1]
South Africa has a high burden of disease, with a high prevalence of HIV and TB. Although evidence is yet to emerge of the effect of SARS-CoV-2 on a population with these pre-existing conditions, there is reason to proceed with caution[2]. There is potential direct and indirect benefit of ACS to people living with HIV and TB, as well as to general public health and the health system preservation.
With the travel lockdown in place, and continued transmission, it appears that South Africa is on the cusp between cluster transmission and community transmission according to WHO’s classification, shown in the table below, indicating that preparation should include temporary hospital facilities and mass critical care.
Key clinical and infection control activities for different transmission scenarios [3]
| No Case | Sporadic Case | Clusters of Cases | Community Transmission | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faculty Space, Including for Transmission | Usual Space. Enhanced Screening and triage at all points of first access to the health system | Dedicated COVID-19 patient care areas within health facility (e.g. infectious disease ward, isolation rooms in emergency or ICU wards). | More patient care areas re-purposed for COVID-19 within the health system, especially for severe cases | Expanded care for severe cases in new hospitals or temporary hospital facilities |
| Staff | Usual space. Enhanced screening and triage at all points of first access to the health system | Dedicated COVID-19 patient care areas within health facility (e.g. infectious disease ward, isolation rooms in emergency or ICU wards) | More patient care areas repurposed for COVID-19 within the health system, especially for severe cases | Expanded care for severe cases in new hospitals or temporary hospital facilities |
| Supplies |
|
|
|
|
| Standard of Care | Usual care with enhanced awareness and recognition of immediate needs for first COVID-19 patients | Usual care and treatment for all patients, including those with COVID-19 | Identify context-relevant core services. Shift service delivery platforms. Consider reduction in elective patient encounters, including elective surgical procedures. | Mass critical care (e.g. open ICU for cohorted patients). |
| Care areas expansion | No requirements for expansion | Designate 10 beds per suspected COVID-19 case | Expand COVID-19 patientcare areas by a factor of 35 | Expand COVID-19 patient care areas by a factor of 58 |
Notes:
- ↑ WHO-2019-nCoV-HCF_operations-2020, https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/331492/WHO-2019-nCoV-HCF_operations-2020.1-eng.pdf
- ↑ The Conversation 2020, https://theconversation.com/tb-hiv-and-covid-19-urgent-questions-as-three-epidemics-collide-134554
- ↑ WHO 2020, https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331492
Quantification of need
At this time there are various parallel initiatives aimed at forecasting the South African epidemic, quantifying the projected need for facilities, and shortfall in existing capacity. At this time, there is no consensus on this. This section will be updated as further data becomes available. ACS will attend to mild to moderately affected COVID-19 patients where basic, targeted medical care will be provided. Should patients’ needs evolve, requiring escalation of care, then transfer of patients from ACS sites to conventional sites of care will be needed as a matter of course, bringing with it logistical challenges and risks. The following pragmatic approach, aligned with the WHO recommended strategic approach, is suggested.
- ACS should be preferably identified with space for expansion. The set-up should be done so that levels of care can be upgraded to higher levels of care.
- This guidance makes the assumption that only uncomplicated COVID-19 cases will be treated at an ACS, entailing that patients with comorbidities, and paediatrics will be referred to conventional facilities. Depending on epidemic trajectory, it may be necessary to expand services to include a greater range of clinical services at ACS.
Strategic approach
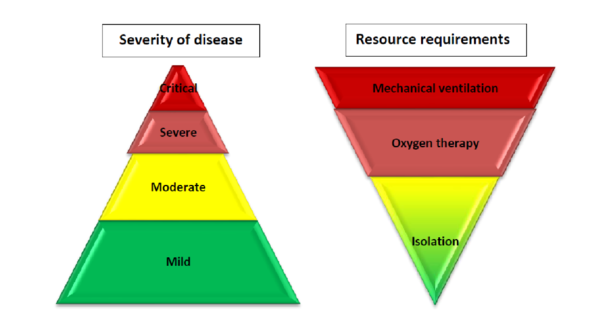
According to WHO, clinical interventions must be put into place immediately, and then scaled up according to the epidemiologic profile.
Under this declared state of disaster, the clinical care strategy which cannot be accommodated within existing facilities, can, on a temporary basis be hosted in ACS:
- Within and around existing healthcare facilities, via reconfiguration and/or augmentation.
- In existing non-healthcare buildings suitable for repurposing, such as universities, hotels and conference centres, warehouses, gyms, hostels etc.
- On open fields, including paved parking areas with rapidly constructed, dismountable structures, such as modular tented structures or using rapid modular construction techniques.
ACS will provide isolation, general (non-acute) care for patients with mild to moderate symptoms and as required, acute care for patients with severe symptoms. Containing confirmed-case patients from general population. Confirmed-case patients can be housed together en masse, while presumptive-case patients must be individually quarantined.
As shown in WHO Strategic approach to clinical care, WHO recommends a range of services to meet patient need. General (non-acute) care ACS model is designed for minimal acuity patients requiring minimal activities of daily living support (e.g. COVID-positive with minimal symptoms or require <2L of oxygen). Acute care ACS model is designed for higher acuity patients requiring closer monitoring or respiratory support (e.g. COVID-positive with pneumonia or respiratory distress requiring ventilator support). Paediatric patients are to be accommodated in separate wards, where strictly controlled visitation may be allowed.
As a preliminary estimate, the following ratios of service is proposed:

| Case severity, risk factors[footnotes 1] | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Mild | Patient should be instructed to self-isolate and contact COVID-19 information line for advice on testing
and referral. |
| Moderate, with no risk factors | Test suspected COVID-19 cases according to diagnostic strategy. Isolation/ cohorting in:
(i.e. adjacent COVID-19 designated health post/EMT-type 1, telemedicine)
|
| Moderate, with risk factors | Patient should be instructed to self-isolate and call COVID-19 hotline for emergency referral as soon as possible |
| Severe | Hospitalization for isolation (or cohorting) and inpatient treatment. |
| Critical | Hospitalization for isolation (or cohorting) and inpatient treatment. |
* Known risk factors for severe COVID-19: age over 60 years, hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory
- ↑ Test suspect COVID-19 cases according to diagnostic strategy
disease, immunocompromising conditions.
Note: Probable cases should be retested immediately.
Typology dictates
To meet the requirements set out in this guidance, prospective “host” sites should be carefully evaluated. The type of “host” site selected will strongly influence or dictate the choice of ACS service model. Some typological responses and service model are set out in precedent examples, shown below.
SARS ACS precedents
Site type: Existing Hospital
Response: Minor Adaptive Reuse
Service Model: Clustered Cohort
Sung-Shan Military Hospital Taipei[1]
Conversion of existing non-isolation buildings to isolation wards for treatment of SARS patients. Steps for conversion and implementation described. Nosocomial infection rate 0.6% ascribed to non-compliance with procedures.
Infrastructure steps taken: 1) Clear buildings of people & equipment. 2) Fans (commercial grade 3X1m blaes, 65W, 60Hz) above each window. 3) plug doors to create negative pressure relative to corridor (0.028-0.07 water gauge in rooms to 0.0 in corridors.) 4) Close stairways between floors. 5) creating three zones at the ground floor for entry A: clean zone for changing and administration; B: Intermediate zone for removing inner layer of PPE, showering; C: contaminated zone for removing outer layer of PPE; 6) cleaning regime described. 7) Patient transport described; 8) Treatment of SARS patients and handling of equipment described: Interesting: Centralize facilities to better control / train health care workers and nosocomial infections
Response: Augmentation
Service Model: Mass ICU
Richmond University Medical Center in West Brighton[2]
A medical tent is stationed outside Richmond University Medical Center in West Brighton

Site type: Existing Hotel
Response: Minor Adaptive Reuse
Service Model: Obligate - Cellular/ single room
Site type: Conference Centre
Response: Repurposing
===== Service Model: Mass ICU =====
NHS Nightingale Hospital London[5], Javits Center New York[6], Los Angeles Convention Centre[7]
Site type: Open Field
Response: Modular Construction
Service Model: Cellular / Single Room
Volumetric Building Companies (VBC) Philadelphia[8] (Linear format)
MAII – USA (Clustered configuration)[9]
Site type: Open Field
Response: Tented Construction
===== Service Model: Mass ICU =====
Central Park, New York [10]
Notes:
No site is likely to meet all requirements and recommendations set out in this document. Adaptations and compromises will be necessary. The examples set out above demonstrate that a variety of host settings are workable, provided that the appropriate utility can be contrived. Services should be provided on site where it is pragmatic to do so, for example where similar services are provided. Outsourcing can also be practical/feasible for some services, such as laboratory services, catering and laundry, provided suitable logistical arrangements can be made.
- ↑ Fung, C., Hsieh, T., Tan, K., Loh, C., Wu, J., Li, C., . . . Lee, C. (2004). Rapid Creation of a Temporary Isolation Ward for Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome in Taiwan. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 25(12), 1026-1032. doi:10.1086/502339 [1]
- ↑ Joseph Ostapiuk, 2020 https://www.silive.com/coronavirus/2020/03/staten-island-hospitals-boosting-capacity-to-meet-potential-coronavirus-scenarios.html
- ↑ Salus, 2020, https://www.salus.global/article-show/architecture-a-critical-ingredient-of-pandemic-medicine
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Shroer, 2020 https://www.ashe.org/what-if-we-used-hotel-patients
- ↑ https://www.bbc.com/news/in-pictures-52092253
- ↑ KATHARINE KEANE 2020, These Architects Are Addressing COVID-19 Health Care Infrastructure Capacity
- ↑ Annlee Ellingson 2020, L.A. Convention Center transforming into a field hospital during coronavirus crisis, [2]
- ↑ Mike Beirne, 2020https://www.probuilder.com/modular-builders-mobilize-deliver-prefab-modules-coronavirus-care
- ↑ Courtesy Philip Patrick Sun
- ↑ https://www.nbcnews.com/health/health-news/live-blog/2020-04-01-coronavirus-news-n1173686/ncrd1174261#blogHeader
ACS Planning Team
A planning team should be formalised to establish the minimum planning and operational requirements for the ACS and to liaise with the local community. The team should include individuals with expertise in the following areas (ideally with knowledge of healthcare delivery under emergency conditions):
- Disaster response / emergency management coordination,
- Clinical care and staffing,
- Facility set-up, operations and management,
- Security,
- Transport (patient, staff),
- Engineering and project management,
- Procurement and coordination of supplies, equipment and pharmaceuticals, and
- Community liaison to ensure that concerns of the adjacent population on understood an addressed.
It is important to ensure compliance with health, safety and building regulations, by ensuring the involvement of relevant local authorities. Stakeholder engagement should be formally documented. Concerns and grievances should be systematically addressed.
Site selection
When selecting a site, the National Department of Health COVID-19 - Guideline Room List for Planning a Temporary Hospital can be utilised to determine whether the site is suitable for a 100, 1000 or 2000 bed facility, as required. The following indicative minimum site sizes are needed:
- 100 Bed ACS/ hospital conversion, requires ± 4 300 m2
- 1000 Bed ACS/ hospital conversion, requires ± 17 600 m2
Evaluation should be done by examining plans (if available), satellite images, drone images, scans and by physical inspection (walkabout). A comprehensive photographic survey should be undertaken and retained for record purposes on the site inspection. This will serve as an audit record and may assist in returning the site to its original function on ACS decommissioning and closure. When scrutinising documents and conducting site inspections to confirm suitability of a site to host an ACS, the following criteria should be taken into account.
Criteria
- Affordability (costs, including operational costs known and budget identified),
- Sufficient physical space and capacity to house the immediate need, with the potential to accommodate physical space requirements. For example, open site solutions should not be sloping,
- Legal rights and encumbrances, including renewal opportunity,
- Free from clear and present danger,
- Outside attenuation zones, floodplains,
- Outside high wind zones,
- Structure in good repair,
- Access to sufficient capacity for
- potable water,
- adequate drainage,
- telephone and/or wifi,
- electricity, and
- Likelihood of acceptance of hosting an ACS by the adjacent and local community
Desirable
- A zone for cleaning, disinfection, and decontamination of equipment at least 15 metres away from occupied areas with access to water, a hard impervious surface and drying areas in the sun, with runoff discharge into the sewer and not into marine ecosystems or the environment.
- Capacity for expansion.
- Accessible to at least two roadways to provide continued access in the event that one roadway becomes blocked on inaccessible.
Infection prevention and control
General guidance for COVID-19 Infection Prevention and Control can be accessed here
Infection prevention and control in the context of COVID-19 should respond to transmission routes of primary concern for the pathogen of interest (contact and droplet transmission, and management of risk waste) as well as infection risk of a general nature (water and sewerage, airborne transmission – under high TB/HIV burden, and general waste). In addition to satisfying standard precautions, transmission-based precautions should focus on three pillars: exposure reduction by spatial configuration, operational strategies, and personal protection.
Transmission-based precautions
Contact and droplet spread: Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 virus occurs via contact and droplet spread. The virus has been shown to persist on surfaces for extended periods of time and is known to be efficient at infecting people.
Medical waste and linen: As SARS-CoV-02 is carried in body fluids and faecal matter, disposal of contaminated items (tissues) and cleaning regimes (spaces, garments, linen) should be accommodated carefully in the workflow design and infrastructure provision. A site specific waste management plan should be formulated in accordance with a site-specific waste management plan with reference to SANS 10248.
Standard precautions
Water and sewerage contamination: The International Water Association concluded that water and sewerage contamination is not considered to be a key risk factor for COVID-19. The panel expressed concern for “how waste and specifically wastewater (medical) would be handled by places (e.g., hostels, hotels) that are used to serve as interim COVID-19 quarantine or testing facilities or accommodation ([ACS]. These are places other than hospitals that are used in the interim for such purposes and do not usually handle wastewater from medical settings. Such facilities should be monitored carefully.”
Airborne transmission: Under exceptional circumstances the risk of airborne transmission arises for SARS-CoV-2, as tabulated below.
| Why it this even in a Table |
|---|
|
As SARS-CoV-2 is not considered airborne, respiratory protection against airborne transmission is not considered necessary, except where aerosolisation of particles may be a risk. According to CDC
According to doctors in the field also when performing
|
![Covid19 Hotel Facility.png [4]](/images/thumb/2/2f/Covid19_facility.png/120px-Covid19_facility.png)