Materials and finishes: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
Furthermore, the South African National Standards (SANS 10400) addresses numerous aspects involving materials and finishes. (Refer to, among others - Parts J, K, L and T in respect of moisture penetration, fixing heights, structural stability and assembly.) Current South African National Standards applicable are as follows: | Furthermore, the South African National Standards (SANS 10400) addresses numerous aspects involving materials and finishes. (Refer to, among others - Parts J, K, L and T in respect of moisture penetration, fixing heights, structural stability and assembly.) Current South African National Standards applicable are as follows: | ||
SANS 204 | SANS 204 Energy-Efficiency in buildings general | ||
SANS 622 | SANS 622 Gypsum cove cornice | ||
SANS 637 | SANS 637 Wood-wood panels (cement-bonded) | ||
SANS 640 | SANS 640 Flexible PU-foams | ||
SANS 803 | SANS 803 Fibre cement boards | ||
SANS 1039 | SANS 1039 Wooden ceiling and panelling boards | ||
SANS 1381 | SANS 1381 Materials for thermal insulation boards | ||
SANS 1508 | SANS 1508 Expanded polystyrene thermal insulation boards | ||
SANS 1783 | SANS 1783 Softwood brandering and battens | ||
SANS 6013 | SANS 6013 Dimensional and mass stability of particle boards with varying humidy | ||
SANS 6016 | SANS 6016 Transverse tensile strength of particle boards | ||
SANS10177 | SANS10177 Fire-testing of materials | ||
The Standard refers to the following definitions: | The Standard refers to the following definitions: | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
==Scope== | ==Scope== | ||
A ceiling in any facility forms the third dimension in any given room area, along with the walls and the floor, and it sometimes separates the roof space from the occupied area below. The manner in which the ceiling is finished will affect not only the acoustics, but also the aesthetics of a room. Certain materials also contribute to the thermal properties of a room. | A ceiling in any facility forms the third dimension in any given room area, along with the walls and the floor, and it sometimes separates the roof space from the occupied area below. The manner in which the ceiling is finished will affect not only the acoustics, but also the aesthetics of a room. Certain materials also contribute to the thermal properties of a room. | ||
[[File:Ceiling.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Ceiling.png|thumb|none|338x338px]] | ||
Ceiling: “upper interior surface of a room or similar compartment, including all materials comprising such surface” | Ceiling: “upper interior surface of a room or similar compartment, including all materials comprising such surface” | ||
| Line 115: | Line 115: | ||
The compliance with SANS fire requirements for a noncombustible ceiling/roof structure will be paramount in determining what ceiling types (and subsequent structure) can be used here. There is the usefulness of the ceiling void above in this type of installation, with more flexibility here for service outlets to be changed if the ceiling is skimmed and painted on completion. Certain nail-up ceilings also have thermal properties in themselves and would not require a separate application of insulation. | The compliance with SANS fire requirements for a noncombustible ceiling/roof structure will be paramount in determining what ceiling types (and subsequent structure) can be used here. There is the usefulness of the ceiling void above in this type of installation, with more flexibility here for service outlets to be changed if the ceiling is skimmed and painted on completion. Certain nail-up ceilings also have thermal properties in themselves and would not require a separate application of insulation. | ||
[[File:Membrane fixed directly to the structure overhead.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Membrane fixed directly to the structure overhead.png|thumb|none|344x344px]] | ||
3. Membrane suspended from the structure overhead allowing a ceiling void above – for example a suspended grid ceiling | 3. Membrane suspended from the structure overhead allowing a ceiling void above – for example a suspended grid ceiling | ||
The suspended ceiling, especially if consisting of modular tiles – available in varying types, allows the most flexibility for positioning lights, ventilation and other services. Replacement of damaged areas is simple and there is easy access to the services running in the void making this option a common choice. | The suspended ceiling, especially if consisting of modular tiles – available in varying types, allows the most flexibility for positioning lights, ventilation and other services. Replacement of damaged areas is simple and there is easy access to the services running in the void making this option a common choice. | ||
[[File:Membrane suspended from the structure overhea.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Membrane suspended from the structure overhea.png|thumb|none|329x329px]] | ||
Each type gives rise to different options in terms of finishes and materials and each has its place in healthcare facilities. | Each type gives rise to different options in terms of finishes and materials and each has its place in healthcare facilities. | ||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
!Material | !Material | ||
!Embodied Energy in MJ / kg (million joules per kilogram) | !Embodied Energy in MJ / kg (million joules per kilogram) | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Extruded anodised aluminium(virgin) | |Extruded anodised aluminium(virgin) | ||
|227 | |227 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
|42.9 | |42.9 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fibre-cement board | |Fibre-cement board | ||
|9.5 | |9.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Fibreglass insulation | |Fibreglass insulation | ||
|30.3 | |30.3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Gypsum plaster | |Gypsum plaster | ||
|4.5 | |4.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Plasterboard | |Plasterboard | ||
|6.1 | |6.1 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Concrete (in situ) | |Concrete (in situ) | ||
|1.0 - 1.6 | |1.0 - 1.6 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 169: | Line 169: | ||
|8.0 | |8.0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Steel (virgin) | |Steel (virgin) | ||
|32 | |32 | ||
|- | |- | ||
|PVC | |PVC | ||
|70 | |70 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
*Disposal | *Disposal | ||
[[File:Product life sustainability.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Product life sustainability.png|thumb|none|402x402px]] | ||
The Green Building Council of South Africa has developed Green Star TM rating tools which will credit materials with the following: | The Green Building Council of South Africa has developed Green Star TM rating tools which will credit materials with the following: | ||
| Line 219: | Line 219: | ||
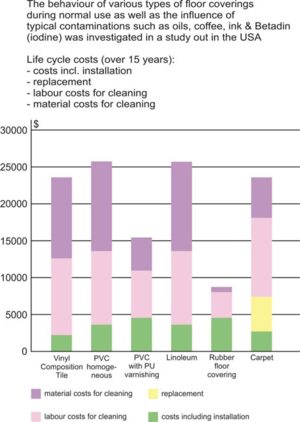
As a practical example, and to indicate the benefit of comparing life cycle costing, the table alongside shows the comparative life cycle costs of various floor finishes - in this instance demonstrating the low life cycle costs of a rubber product, even though the installation cost for this product was the highest at the outset. | As a practical example, and to indicate the benefit of comparing life cycle costing, the table alongside shows the comparative life cycle costs of various floor finishes - in this instance demonstrating the low life cycle costs of a rubber product, even though the installation cost for this product was the highest at the outset. | ||
[[File:Life cycle costing and sustainability diag.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Life cycle costing and sustainability diag.png|thumb|none|365x365px]] | ||
===Toxicity and effect on indoor environment=== | ===Toxicity and effect on indoor environment=== | ||
| Line 293: | Line 293: | ||
While this issue may not affect the selection of a ceiling finish, there are principles to be borne in mind when establishing what finish is best in high-risk environments. | While this issue may not affect the selection of a ceiling finish, there are principles to be borne in mind when establishing what finish is best in high-risk environments. | ||
[[File:Selection criteria diag.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Selection criteria diag.png|thumb|none|360x360px]] | ||
Below is a table adapted from NSW Health: Infection Control Policy (PD 2007-035), which sets out patient risk categories: | Below is a table adapted from NSW Health: Infection Control Policy (PD 2007-035), which sets out patient risk categories: | ||
| Line 329: | Line 329: | ||
Whether the materials/finish of a ceiling can be cleaned thoroughly will define the extent to which infectious agents can be prevented from multiplying on a surface. Some materials can tolerate a reasonable amount of moisture, facilitating regular washing, while others would be adversely affected by it and can only be dusted or wiped. | Whether the materials/finish of a ceiling can be cleaned thoroughly will define the extent to which infectious agents can be prevented from multiplying on a surface. Some materials can tolerate a reasonable amount of moisture, facilitating regular washing, while others would be adversely affected by it and can only be dusted or wiped. | ||
[[File:Cleaning and maintenance diag.jpg|thumb|none]] | [[File:Cleaning and maintenance diag.jpg|thumb|none|341x341px]] | ||
For cleaning to be effective, the surface must be able to withstand regular and fairly vigorous cleaning, with proper access to all surfaces. Where there are small recesses or difficult to reach corners, dirt is easily trapped providing dark, undisturbed conditions – the perfect breeding area for bacteria. | For cleaning to be effective, the surface must be able to withstand regular and fairly vigorous cleaning, with proper access to all surfaces. Where there are small recesses or difficult to reach corners, dirt is easily trapped providing dark, undisturbed conditions – the perfect breeding area for bacteria. | ||
| Line 771: | Line 771: | ||
==Performance categories== | ==Performance categories== | ||
The properties described in the selection criteria in Section C above have been listed in the table below, and then grouped into five performance categories that would satisfy the requirements in various areas within a healthcare facility | The properties described in the selection criteria in Section C above have been listed in the table below, and then grouped into five performance categories that would satisfy the requirements in various areas within a healthcare facility | ||
[[File:Performance category.png|thumb|none]] | [[File:Performance category.png|thumb|none|535x535px]] | ||
*Skimmed or plastered and painted – seamless ceiling | *Skimmed or plastered and painted – seamless ceiling | ||
| Line 797: | Line 797: | ||
| rowspan="2" |'''Department''' | | rowspan="2" |'''Department''' | ||
| rowspan="2" |'''Room Name''' | | rowspan="2" |'''Room Name''' | ||
| colspan=" | | colspan="5" |'''Ceiling Performance''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" |'''1 2 3 4''' | | colspan="4" |'''1 2 3 4''' | ||
|'''5''' | |'''5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="22" |'''Acute In-patient Wards (Adults)''' | | rowspan="22" |'''Acute In-patient Wards (Adults)''' | ||
| Line 1,122: | Line 1,121: | ||
| colspan="5" |'''Ceiling Performance''' | | colspan="5" |'''Ceiling Performance''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="5" | '''1 2 | | colspan="5" | '''1 2 3 4 5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="12" | | | rowspan="12" | | ||
| Line 1,494: | Line 1,493: | ||
| colspan="5" |'''Ceiling Performance''' | | colspan="5" |'''Ceiling Performance''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="5" | '''1 2 3 | | colspan="5" | '''1 2 3 4 5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="14" | | | rowspan="14" | | ||
| Line 1,873: | Line 1,872: | ||
| rowspan="2" |'''Department''' | | rowspan="2" |'''Department''' | ||
| rowspan="2" |'''Room Name''' | | rowspan="2" |'''Room Name''' | ||
| colspan=" | | colspan="5" |'''Ceiling Performance''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | | colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | ||
|'''5''' | |'''5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 2,242: | Line 2,240: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | | colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | ||
|'''5''' | |'''5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="4" | | | rowspan="4" | | ||
| Line 3,360: | Line 3,358: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | | colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | ||
|'''5''' | |'''5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="11" | | | rowspan="11" | | ||
| Line 3,738: | Line 3,736: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | | colspan="4" | '''1 2 3 4''' | ||
|'''5''' | |'''5''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| rowspan="12" | | | rowspan="12" | | ||
Latest revision as of 15:05, 27 October 2020
Internal Ceiling Finishes in Healthcare Facilities
Context
Overview – finishes in the healthcare environment
Interior finishes play a vital role in a healthcare facility, as proper wall treatments can contribute to the creation and maintenance of a positive therapeutic environment for patients (Mayer, 2005)
Building finishes account for a large proportion of the overall cost of constructing a healthcare facility. According to Shohet et al. (2002), interior finishing and interior construction account for 32% of the initial budget. Maintenance and cleaning of finishes add substantially to the ‘whole-life costs’ of finishes within a hospital or healthcare facility.
Despite this, finishes are often treated as optional and purely aesthetic components of the building and the spaces within it. When budget constraints are implemented, the finishes are usually the first area to suffer. Institutions will often standardise finishes across a spectrum of rooms/facilities for economy in replacement and/or cleaning regimes.
Interior finishes, however, play a vital role in the health care environment, and contribute substantially to the delivery of healthcare service and the protection of staff and patients.
In a study conducted by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP (PwC) in association with the University of Sheffield and Queen Margaret University College, 2004, the comments from the majority of people who visited hospitals, including staff and patients, included “cold, depressing, dehumanising, Kafkaesque, dirty, smelly, frightening, impersonal, confusing, dull shabby, windowless, grim, stressful…” While the fact that most patients interviewed may have been negative as a result of their being ill, it does highlight a problem of the inhumane and threatening appearance of hospital environments (historically) where even more attention should be paid to creating a caring atmosphere.
It is this paradigm shift that is required when considering and selecting finishes. The role of finishes in a healthcare facility has become as important an aspect of design as room sizes and relationships.
“UNTIL THE GERM THEORY WAS DEVELOPED, MORE MEN WERE DYING FROM SMALL WOUNDS AND DISEASES THAN FROM MAJOR TRAUMAS ON THE FRONTLINES. BUT AS SOON AS GERM THEORY WAS DEVELOPED A WHOLE NEW PARADIGM, A BETTER WAY OF UNDERSTANDING WHAT WAS HAPPENING
Building finishes are usually seen as a separate and final application to the building structure (Dean, 1996). There are, however, instances where the finish is integral to the structure. These documents therefore include finishes and materials in such cases.

Suite of documents
This document forms part of a series of documents addressing internal materials and finishes in health facilities, which in turn form part of the suite of documents created under the IUSS Project. The aim of the Materials and Finishes Suite of Documents is to provide guidance on design and specification for the various building components where current legislation, including the National Building Regulations does not adequately cover suitability of finishes in the healthcare facility context.
While the guidelines speak mostly of new building work, most of the principles are consistent with refurbishment projects to existing buildings as well.
How to use this document:
- Review the Selection Criteria - Part B
- Select a Room / Department name in Part D, and note Performance Category
- Refer to Table 1 for the Properties that make up that Performance category
- Refer to Part C to assess ceiling types that could satisfy those performance requirements.
Other IUSS HEALTH FACILITY GUIDES in this series include:
- Internal Floor Finishes (draft document rev 5)
- Internal Wall Finishes (draft document rev 4)
- Joinery and Storage Systems (to follow)
- Doors and Ironmongery (to follow)
- Sanitary Ware (to follow)
- Signage and Wayfinding (to follow)
These guidelines are updated and revised periodically, and can be accessed at www.iussonline.co.za
The primary objective of this technical guide is to assist decision-makers with the selection of ’appropriate’ ceiling finishes in the health facility context.
The guide looks at the context (Part A), then examines various selection criteria (Part B), then summarises technical information of various ceiling finishes (Part C) to assist with assessing the best finish for the facility. Finally, the selection criteria are grouped together to form performance categories (Part D) and a matrix of rooms with the most relevant performance category is indicated.
Policy context
This document offers guidance on the selection of appropriate ceiling finishes in health facilities. While the aim is to inform project and design teams about the wide range of considerations to take into account when selecting finishes, it does not diminish the responsibility of the design team to comply with all applicable professional and regulatory obligations and to specify materials and finishes ‘fit for purpose’.
Some of the pertinent regulations are as follows:
- National Building Regulations and Building Standards ACT, 1977 (Act 103 of 1977) amended 30 May 2008
- SANS 10400, Code of Practice for the application of the National Building Regulations, first rev. August 1990
- R158, Government Notice dated Feb 1980 (updated March 1993) Regulation pertaining to control of Private Hospitals, (revised 05 November 1996, but not gazetted)
- R187, Regulations Governing Private Health Establishments, Western Cape, 22 June 2001
The design principles on the above documents must be taken into account alongside the recommendations of this document. For example: Clause 32 of the R158 states under general requirements in the OT Unit that the ceiling must be dustproof, of smooth impervious material, painted white or light-coloured suitable washable paint.
Furthermore, the South African National Standards (SANS 10400) addresses numerous aspects involving materials and finishes. (Refer to, among others - Parts J, K, L and T in respect of moisture penetration, fixing heights, structural stability and assembly.) Current South African National Standards applicable are as follows:
SANS 204 Energy-Efficiency in buildings general
SANS 622 Gypsum cove cornice
SANS 637 Wood-wood panels (cement-bonded)
SANS 640 Flexible PU-foams
SANS 803 Fibre cement boards
SANS 1039 Wooden ceiling and panelling boards
SANS 1381 Materials for thermal insulation boards
SANS 1508 Expanded polystyrene thermal insulation boards
SANS 1783 Softwood brandering and battens
SANS 6013 Dimensional and mass stability of particle boards with varying humidy
SANS 6016 Transverse tensile strength of particle boards
SANS10177 Fire-testing of materials
The Standard refers to the following definitions:
Other provincial policy documents are also applicable:
- KwaZulu-Natal, Department of Health Policy Document for the Design of Structural Installations, Rev.7, January 2013
- Eastern Cape Department of Roads and Public Works and Department of Health Hospital Design Guide, revised. August 2004
Selection Criteria
Scope
A ceiling in any facility forms the third dimension in any given room area, along with the walls and the floor, and it sometimes separates the roof space from the occupied area below. The manner in which the ceiling is finished will affect not only the acoustics, but also the aesthetics of a room. Certain materials also contribute to the thermal properties of a room.
Ceiling: “upper interior surface of a room or similar compartment, including all materials comprising such surface”
Roof assembly: “building cover and its supporting structure, including any ceiling attached to such structure, including any additional components such as insulation”
Although ceilings are for the most part out of reach of hands and feet of everyday staff and patient traffic, and the microbial burden would seem to be somewhat reduced, airborne dust particles and fine moisture dispersal can still allow pathogens to gather on ceiling surfaces. The ceiling can therefore have a role to play in infection prevention and control.
Ceilings are often the membrane onto which services such as lighting or air-conditioning, and a host of other fittings, are fixed, while obscuring unsightly services behind. These and other criteria will be discussed in more detail under Selection Criteria.
Generally, the ceiling type falls into one of three types in terms of installation:
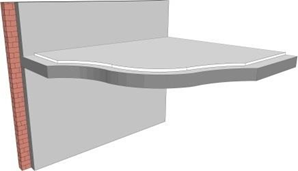
1. Actual Soffit of structure overhead – for example a concrete slab
While this type of installation will limit the flexibility of service outlets, it provides a solid structure where heavier fittings need to be attached to the ceiling. The finishes can range from off-shutter smooth concrete to plastered and painted surface treatment.
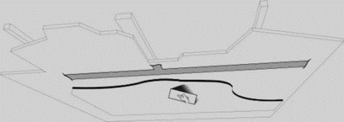
2. Membrane fixed directly to the structure overhead – for example a nail-up ceiling board
The compliance with SANS fire requirements for a noncombustible ceiling/roof structure will be paramount in determining what ceiling types (and subsequent structure) can be used here. There is the usefulness of the ceiling void above in this type of installation, with more flexibility here for service outlets to be changed if the ceiling is skimmed and painted on completion. Certain nail-up ceilings also have thermal properties in themselves and would not require a separate application of insulation.
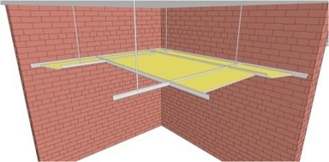
3. Membrane suspended from the structure overhead allowing a ceiling void above – for example a suspended grid ceiling
The suspended ceiling, especially if consisting of modular tiles – available in varying types, allows the most flexibility for positioning lights, ventilation and other services. Replacement of damaged areas is simple and there is easy access to the services running in the void making this option a common choice.
Each type gives rise to different options in terms of finishes and materials and each has its place in healthcare facilities.
Environmental aspects in the choice of finishes
A guide of finishes would be incomplete without highlighting the environmental aspects in the choice of finishes.
This is an extremely broad factor covering:
- Embodied energy of materials
- Life cycle costing/sustainability
- Toxicity and effects of indoor environment quality
Embodied energy of materials
| Material | Embodied Energy in MJ / kg (million joules per kilogram) |
|---|---|
| Extruded anodised aluminium(virgin) | 227 |
| Extruded anodised aluminium (recycled) | 42.9 |
| Fibre-cement board | 9.5 |
| Fibreglass insulation | 30.3 |
| Gypsum plaster | 4.5 |
| Plasterboard | 6.1 |
| Concrete (in situ) | 1.0 - 1.6 |
| Concrete (precast) | 2.0 |
| Cement | 7 - 8 |
| Particle board | 8.0 |
| Steel (virgin) | 32 |
| PVC | 70 |
| Paint (solvent-based) | 98.1 |
Source: Alcorn and Wood, 1998.The term embodied energy refers to the total energy measure required to manufacture a product. This includes:
- Harvesting/mining of the raw material
- Processing the material
- Manufacturing the product
- Transport/delivery of the product to the manufacturing plant, retail outlets and finally the end user
- Labour or mechanical energy spent on placing the product in its finished position
Buying locally-produced materials is an easy and achievable way to lower embodied energy of a building. The table below gives an indication of the embodied energy of various typical building materials.
Embodied energy of common ceiling materials (finish and substrates)
While health facility design may limit your selection of materials in terms of other performance factors, which are more critical, every opportunity to reduce the embodied energy of materials should be pursued. Manufacturers are increasingly aiming at reducing embodied energy, as well as the carbon footprint in the manufacture of their products.
This is driven by the market demand and designers can contribute by choosing materials that support green initiatives in this regard.
Life cycle costing and sustainability
Life cycle costs are described as the social, economic and environmental costs of a material or product from cradle to grave – that is, from the extraction of the raw ore needed to make it, through the manufacturing, to the end use to disposal or recycling. (Daniel D. Chiras)
The durability of materials is a key element in the life cycle cost assessment. A product may have a low embodied energy, but requires more frequent replacement in the building.
Specifiers should investigate the service life of materials with the respective manufacturers, to establish its life span. This element should also be highlighted to funders who often place more emphasis on reducing the capital cost of a facility, without considering the long-term cost.
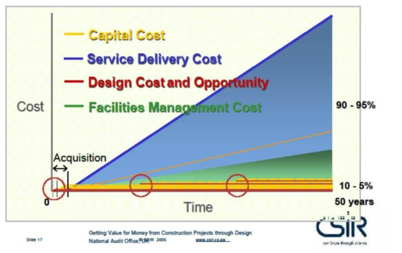
The graph below indicates how capital outlay costs compare to life span costs – emphasising the importance of life cycle costs.
Sustainability should be considered in all four stages of product life:
- Manufacture
- Use
- Maintenance
- Disposal
The Green Building Council of South Africa has developed Green Star TM rating tools which will credit materials with the following:
- Reuse of existing material
- Recycling properties
- Local sourcing
As a practical example, and to indicate the benefit of comparing life cycle costing, the table alongside shows the comparative life cycle costs of various floor finishes - in this instance demonstrating the low life cycle costs of a rubber product, even though the installation cost for this product was the highest at the outset.

Toxicity and effect on indoor environment
VOCs can cause irritation and odour annoyance and could lead to behavioral, neurotoxic, hemotoxic and genotoxic effects (Meininghaus et al., 2000; Hoskins, 2003; Hodgson et al., 2000)
Indoor Environment Quality (IEQ) is one of the nine categories of the Green Building Council of South Africa’s Green Star TM Rating Tools. These rating tools are used to assess environmental performance of a building and/or materials and through improvement in IEQ, the wellbeing of the occupant is protected.
IEQ is measured in terms of:
- Internal noise levels (this is discussed in more detail under Selection Criteria: Acoustics)
- Mould prevention (this is discussed in more detail under Section Criteria: Humidity)
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Materials such as paints and polyvinylchlorides can emit VOCs (gasses) when finishes are new and these reduce over the life span of the product. Sealants and adhesives also give off VOCs, having a negative effect on indoor air quality.
According to Hoskins (2003), VOCs can be carcinogenic, depending on the compound. When considering the toxic impact on the environment in which the various ceiling finishes will be installed, the finish as a whole - complete with painted or surface finish, substrate material and any adhesives used – must be taken into account.
A further important aspect to consider is the use of non-toxic materials in mental health facilities, where patients are prone to chew and ingest any materials that can be uplifted off surfaces, from paint to flooring, to ceiling panels where these are within reach.
Every effort must be made when specifying materials and finishes in these facilities to ensure that materials and their junctions are wellsecured and cannot be peeled back or picked off by patients. The toxicity of the material content should also be clarified with manufacturers to ensure that these materials are safe and fit for this purpose.

Evidence-based design
Determining which criteria to apply when selecting finishes appropriate for health facilities could be very subjective. However, in recent years, there have been substantial advances made by various researchers in providing scientific evidence for the impact of the healthcare environment on healthcare outcomes. Many studies, such as Ulrich et al. (2008) demonstrated connections between the design of facilities and the effect on patients, staff and the public utilising healthcare buildings. This has led to a growing understanding of what are priorities in designing health facilities:
Extensive research by The Centre for Health Design (CHD) Research Coalition on Evidence-based Design literature led to the Evidence-based Design Glossary, (Phase 1 Report Healthcare Environmental Terms and Outcome Measures) November 2011.
Various unrelated research papers were gathered with interesting results. These included the following:
- Environmental factors influencing the contamination of inanimate surfaces (including interior finish materials of flooring and furniture as well as surface cleaning methods) Anderson, Mackle, Stoler and Mallison 1982, and Lankford, Collins, Youngberg, Rooney, Warren and Noskin 2006)
- Reducing background noise in operating theatres and the impact on surgical errors (Moorthy, Munz, Dosis, Bann and Darzi, 2003)
- Multiple environmental factors affecting patient fall rates (Calkins, Biddle and Biesan, 2011 and Becker et al., 2003)
- Patient satisfaction with quality of care when sound-reflecting ceiling tiles were replaced with sound-absorbing tiles to reduce noise (Hagerman and Colleagues, 2005)
- Positive visual distractions including windows, nature photographs, etc. and the effect on patients restless behaviour in waiting rooms (Nanda, 2010, Pati and Nanda, 2011)
- Nurses’ exposure to daylight correlating to job satisfaction (Alimoglu and Donmez, 2005)
- Noise as a source of stress and its negative impact on staff (Morrison, Haas, Shaffner, Garett and Fackler, 2003)
- Textile materials containing microbial agents (Takai et al., 2002)
- Aesthetic appeal and its effect on patient and staff satisfaction and patient waiting (Becker and Douglass, 2008)
Arising out of an overview of these studies, the following selection criteria have been identified:
- Infection prevention
- Cleaning and maintenance
- Safety
- Indoor air quality - humidity
- Indoor air quality - emissions
- Acoustics
- Aesthetics
Although all these factors are important, the specific functions of each space or room will re-order the priority of fulfilling each aspect. To assist with establishing these priorities and assessing the effects of each criterion, these are examined in more detail in the next section.
Selection criteria
Infection prevention
The South African Patients’ Rights Charter (1997) states: “Everyone has the right to a healthy and safe environment that will ensure their physical and mental health or well-being including … protection from all forms of environmental danger, such as pollution, ecological degradation or infection.”
The selection of a suspended ceiling must be approved by the infection control team so that it does not become a microbiological hazard. (Scottish R & D Project: B (04)02)
According to a survey conducted by Rohde (2002), materials and finishes have in the past been selected according to the following characteristics in declining order of importance: Aesthetics, durability, ease of maintenance, client preference, initial cost, cost of maintenance, infection control, ease of installation and life cycle cost.
Selecting the correct finish is a complex process with many aspects to consider, and the many and varied room types in a health facility extend the options. However, in healthcare facilities, the importance of the effect of a particular finish on the prevention of infection control must be prioritised.
While it is understood that not every area of a hospital or health facility will carry infection prevention as the highest priority, this aspect remains the most pressing issue in selection of finishes in health facilities.
“Ideal features of surfaces that satisfy sustainability, infection prevention and safe patient outcomes include cleanability, resistance to moisture and reducing the risk of fungal contamination.” (Bartley, 2010 based on CDC and HICPAC Guidelines 2003)
The rising incidence of healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) in hospital and medical facilities supports the view that the selection of materials must first address infection prevention. This impacts the choice of materials in two aspects. The first is whether the surfaces are likely to become reservoirs for infectious agents. This is a function of the surface conditions and structure of the ceiling material. The second is the ability to clean the finish, and this is discussed further in the next section.
The Centre for Disease Control in the United States quoted statistics in 2010 of one out of every 20 hospitalised patients contracting HAIs, particularly in relation to sepsis and pneumonia.
Although there is no known direct evidence linking HAIs in patients to particular finishes, there have been numerous studies conducted on microbial counts on floor finishes – particularly in soft textiles such as carpets. Beyer and Belsito (2000) proved that carpet acted as a reservoir for fungi and bacteria.
Anderson et al. (1982) also carried also carried out microbiological studies comparing patient rooms with and without carpet. The study found higher microbial counts and more E.coli and other organisms on carpet samples than bare floors.
While this issue may not affect the selection of a ceiling finish, there are principles to be borne in mind when establishing what finish is best in high-risk environments.

Below is a table adapted from NSW Health: Infection Control Policy (PD 2007-035), which sets out patient risk categories:
When selecting finishes for a room/area that has an extreme or high infection control risk, special care has to be taken to select an appropriate finish. Although ceilings are out of reach and therefore less affected by regular touching, airborne bacteria can be carried on circulating mechanical ventilation, and aerosol contaminants which are distributed when water is splashed, (Ayliffe et al., 2000) can carry pathogens to ceiling level.
Ceiling materials and finishes that resist the spread of infection will have qualities that can be summarised as follows:
- Smooth
- Impervious
- Joint-less/seamless
On the opposite side of this spectrum, where infection prevention is the lowest priority, ceilings will have the following properties:
- Textured
- Perforated
- Jointed

Certain materials have been shown to inhibit bacterial growth – such as vinyl, PuR and natural materials such as cork. This will also contribute to the prevention of infection. Ceilings with these properties will have the following quality:
- Bacteriostatic
A note about anti-bacterial treatments and additives to ceiling products:
Some manufacturers tout the additional benefit of anti-microbial treatment in paints or grout to combat bacteria. The use of antimicrobial additives in the built environment is growing, for example - the impregnation of wood framing with silver nitrate to prevent microbial and mould growth, and extend the life span of the wood.
Synthetic fibres such as polypropylene textile and vinyl for example, in themselves do no provide a nutrient source which microbes need to survive, but some finishes can trap soil, dust and moisture which do provide that source.
The CDC HICPAC guidelines (CDC 2003) indicate that there is no evidence that antimicrobial-impregnated articles will prevent disease. There is a need for further research on products treated with these chemicals in terms of their potential risks and benefits to healthcare users.
Cleaning and maintenance
Connected with infection prevention is the issue of cleaning. Ceilings tend to have ’reactive’ cleaning regimes, rather than regular cleaning programmes. This is partially because the ceiling gives an impression of cleanliness, but this can be misleading.
Whether the materials/finish of a ceiling can be cleaned thoroughly will define the extent to which infectious agents can be prevented from multiplying on a surface. Some materials can tolerate a reasonable amount of moisture, facilitating regular washing, while others would be adversely affected by it and can only be dusted or wiped.

For cleaning to be effective, the surface must be able to withstand regular and fairly vigorous cleaning, with proper access to all surfaces. Where there are small recesses or difficult to reach corners, dirt is easily trapped providing dark, undisturbed conditions – the perfect breeding area for bacteria.
Information regarding cleaning materials should also be considered, as solvents and cleaning agents can quickly cause deterioration of the finish if it is not robust enough to withstand the cleaning required.
A further aspect to consider is the disruption that will be required to carry out the cleaning regime and possible maintenance. This is pertinent to areas such as operating theatres that may remain in use 24 hours a day.
Where there is a high requirement for regular cleaning of a ceiling in view of its location in a sensitive area, together with a need for minimal disruption for maintenance, the ceiling properties could be summarised as:
- Washable
- Low maintenance

An additional consideration in the selection of ceiling finishes in health facilities in terms of maintenance is the provision of access to services in the ceiling void. Health facilities will generally require a high concentration of various services, most of which run in the ceiling void.
This will include electrical power and lighting, data, nurse call systems, medical gas and vacuum lines, air-conditioning and extract ducts, as well as hot water and waste pipes to name a few. Although service ducts and shafts can alleviate this congestion in the ceiling, distribution on the horizontal plane will nonetheless be required.
By selecting ceiling types that cater for easy access and giving thought to the best positions for these access panels - even marking these panels where necessary - this will facilitate easier maintenance of in-ceiling services during the life span of the building. This in turn will reduce ’downtime’, and disruption of the health facility.

While the location of access panels is determined by the layout of services, certain rooms or areas will be more suitable for these panels.
- No combustible materials are permitted in ceilings or roof structures for buildings classified as hospitals.
- Medical facilities and healthcare categories are classified separately and have different requirements.
- Strict parameters are given for the depth of ceiling voids and this is related to the need for sprinklers when the voids exceed a given depth.
- Compartmentalisation of the ceiling void is required in area and distance, with fire stops.
- A dedicated section is written regarding operating theatres and intensive, high and critical care units, stipulating 120 min fire resistance for division separations.
- A full list of materials deemed to be non-combustible is provided.
This has been listed as the property:
- Access panels
Safety
Unlike floors which can prevent - or contribute to - falls by patients and staff, ceilings are largely out of reach and need not be assessed for safety as is relevant to floors. The safety aspect of fire performance does however need to be highlighted. The SANS 10400 lists specific requirements for hospitals and medical facilities with regard to ceilings. This is aimed at protecting the patients who are most likely frail, may not be able to walk, and would require assistance and more time to escape in the event of fire.
The definitions in the SANS 10400: Part A read:
- E2 Hospital
Occupancy where people are cared for or treated because of physical or mental disabilities, and where they are generally bedridden.
- E3 Other institutional (residential)
Occupancy where groups of people who either are not fully fit, or who are restricted in their movements or their ability to make decisions, reside and are cared for.
- E4 Healthcare
Occupancy which is a common place of long term or transient living for a number of unrelated persons consisting of a single unit on its own site who, due to varying degrees of incapacity, are provided with personal care services or are undergoing medical treatment.
These requirements are set out in Part T of SANS 10400, and include:
All ceilings in hospitals would need to be non-combustible material. In other health facilities, such as community health centres or clinics, there are exceptions to the non-combustible requirement, subject to compliance with certain conditions. Since each project varies, the advice of a competent fire engineer should be obtained.
Indoor air quality
There are two critical aspects to be considered when selecting floor finishes under the heading of indoor air quality. The first is he effect of the functions in that environment on the flooring material - namely water/moisture in wet spaces, The second is the effect of the material on the floor material - namely the emission of volatile organic compounds.

Humidity
Certain rooms and areas of health facilities are by nature of the function they house - wet spaces. These are spaces specifically used for the purpose of cleaning, washing, bathing or food preparation. These rooms will generate more moisture than others, and as a result will require moisture-resistant finishes. If the ceiling panels or surfaces are hygroscopic, these finishes can be prone to mildew and mould growth. Surfaces must remain dry and clean in order to prevent the growth of fungus. (Hodgson et al., 2000)
Non-porous materials that do not absorb water are essential in these areas. These materials should also withstand regular cleaning, and should be able to withstand regular exposure to the moisture. Indoor air quality (IAQ) may be compromised by microbial contaminants such as mould, bacteria, allergens, chemicals, etc. in the air, which can affect the health of people. Where this is a requirement in a ceiling finish, this property will be listed as:
- High humidity
Emissions from materials
As discussed under Environmental Aspects, the kind of flooring installed can affect the environmental quality of the interior if VOCs are given off by – commonly referred to as off-gassing:
- The product itself, along with its structure
- The adhesives used to fix the product or its layers
- The paints or sealants used to finish
- The cleaning solutions required for regular maintenance

People who work in noisy environments for long shifts day in and day out, also have similar stress-induced experiences. They report everything from exhaustion to burnout, depression and irritability”
The smell of the interior of a new car - enjoyed by many is an example of plasticizers that have evaporated - emissions that affect the indoor air quality. Various methods for measuring VOCs have been developed in recent years since the increase in awareness that these emissions exist and can have an influence on the indoor air quality. The Green Building Council of South Africa (GBCSA) awards points in the IEQ13 category where interior finishes minimise the contribution and levels of VOCs in buildings – with reference to paints, adhesives/sealants and carpets/flooring, where these products meet the IEQ levels’ outlines.
IEQ14 section measured the formaldehyde minimisation which is common with composite wood products. In addition, MAT-7 section recognises the reduction of PVC-products in the building materials used.
It should be noted that primary VOCs decline quickly in the short-term (<1 year), while secondary emissions can continue for the life span of the product, and should also be borne in mind when assessing this aspect of materials. Timing of the testing will yield very diverse results.
Proper moisture control is essential in order to reduce health risks and sick building syndrome in an enclosed space
Patients with respiratory weaknesses such as asthma are most likely to be affected by VOC emissions, and high-risk patients would benefit from materials that do not contribute to their condition. The ultimate goal of reducing emissions in the manufacture of building products should be to create a better and healthier environment for the patients and users of the facility. Materials such as paints and polyvinyl-chlorides can emit VOCs which can have a negative effect on indoor air quality.
According to Hoskins (2003), VOCs can be carcinogenic, depending on the compound. VOCs can also cause irritation and odour annoyance, and could lead to behavioural, neurotoxic, hepatoxic and genotoxic effects (Meininghaus et al., 2000; Hoskins, 2003; Hodgson et al., 2000.)

However, the ‘order of magnitude’ should also be applied when using ‘low VOC emissions’ as a criterion to select finishes. The use of enamel paint on plaster, for example, may result in higher VOC emissions than say, a pre-finished lay-in ceiling board, but the infection control benefits of the seamless finish will outweigh the risks from VOC emissions. (More fatalities in patients have been linked to infection control issues than to VOC emissions issues.) Ceilings often present an opportunity to reduce the heat load on rooms from the roof space through insulation. This could form part of the ceiling material itself or be laid over the ceiling.
Acoustics
Noise in health facilities is mainly generated by:
- Impact sounds e.g., pedestrian and wheeled equipment, bedrails moved up and down, doors closing and opening, footfalls, etc.
- Airborne sounds, e.g., speech, medical equipment bleeps and alarms, nurse calls, PA system, etc.
Acoustical engineers at John Hopkins University found that average (continuous level equivalent, LAeq) daytime hospital noise levels have risen from 57 dBA in 1960, to 72 dBA in 2006, with night-time sounds increasing from 42 dBA to 60 dBA over the same period. (Sound Practices: Noise Control in the Healthcare Environment – Research Summary, 2006, Herman Miller Healthcare). An average motorcycle noise level measures 85 dB. The World Health Organization’s recommended LAeq value for ward areas is 30 dBA.
Studies have shown that high levels of noise have negative physical and psychological effects on patients, disrupting sleep, increasing stress and raising blood pressure levels (Cmiel et al., 2004). The University of Michigan released a news brief in November, 2005 showing that chronic noise increased the risk of heart-attack in patients by 50% for men and 75% for women. The negative effect of chronic noise extends to staff as well. While the presence of electronic devices and healthcare apparatus, designed to give audible signals and alarms to the nursing staff of the patient’s vital signs, architects and health facility planners need to make an effort to minimise this effect of noise and alarm fatigue.

Long straight passages are perfect echo corridors, often amplifying noises. Disturbances in the sound path help limit the sound transmission, for example by creating steps in the ceiling level or changes of direction in the passageways.
Nurses’ stations during shift change are areas where noise levels can reach those similar to jack-hammer levels, according to Cmiel, et al. 2004). Consideration should be given to applying acoustic materials to these areas to maximise sound absorption where possible.
Recesses to accommodate noisy equipment can also be treated acoustically to reduce reverberation. Distance is also a good strategy where feasible as sound intensity decreases with distance, provided that the room dimensions and surfaces are such that there is very little reverberation.
Sound-absorbent ceiling finishes should be used in key areas such as nurses’ rest rooms or waiting areas where infection control requirements would not be as critical. In areas where sound reduction rates highly as a requirement (e.g. ICU and general wards), then this factor would be listed as: High acoustic

Aesthetics
Research results from CABE (2004 and 2005), King’s Fund (2004) and Leather, Beale and Lee (2000) all highlight the need for an integrated, holistic and sympathetic hospital aesthetic.
Key results of a study by Becker and Douglass (2008), show that the physical appearance of the architectural setting, including finishes, has an effect on the patient’s experience as well as the recruitment and retention of staff – happy staff are more motivated to care for patients, who in turn recover more quickly.
Reflectivity of the ceiling material can boost natural light in a room or alternately produce glare - both of which have a direct impact on the comfort levels in the room. By ensuring skylights are oriented correctly, and shaded appropriately, natural light could be introduced through the ceiling.

The ceiling surface finish should complement the function of the room, and monotony for the sake of economics should be avoided, bearing in mind that most patients will be focused on the ceiling for the duration of their stay.
Printed ceiling tiles, or polycarbonate panels with vinyl film images, behind which lighting can be introduced, could be used in key areas. This can transform a dull ward ceiling into a fascinating window to the outside world. CABE (2004) highlights the need for patients to have a ’connection with nature’, and these ceiling ‘windows’ are the ideal opportunity to supplement views to the exterior.
Natural light is a key factor in creating an environment for patient recovery. The occupants of the ward should be considered – paediatric wards are opportunities for playful scenes that will help little patients feel at ease.
In public areas where more emphasis might be placed on an attractive and welcoming interior than other factors, then this factor would be listed as:
• High aesthetics
Technical Information - Ceiling Types
Paint on seamless plaster
General description and properties
Paint is easily applied by roller to a plastered ceiling soffit. The soffit could be constructed from plasterboard sheets, which are then skimmed or from concrete. Note that the structure onto which the plasterboard is fixed would need to be non-combustible if the facility is a hospital. Following a primer and undercoat, usually three coats of paint are applied. Two-coat plaster or skimming is highly recommended prior to painting, as defects will be highlighted with the high-gloss type paints.
Paint types that can be applied to the ceiling soffit will vary between oil-based and water-based types. Enamel paint dries to a hard, glossy, finish. It is usually oil-based. Velvet sheen paints are water-based, but produce a less glossy finish. PVA-paints are also water-based, but produce a matt finish. Paint is fairly inexpensive when compared to other ceiling finishes - excluding the structure.

Infection prevention
The smooth seamless finish produced by painted concrete or plasterboard ceilings, make this finish ideal for areas where infection prevention is paramount. There are no joints or crevices to encourage growth of microbes. Paints with nanotechnology enhancements are also being developed. These paints inhibit the growth of algae and fungus.
Cleaning and maintenance
The enamel and velvet sheen paints are highly washable, durable and stain-resistant. PVA can also be washed, but is not as stain-resistant. Paint is a low maintenance finish which may require re-application every few years, unless latent defects arise.
Access to services
Access panels need to be planned in the structure prior to painting. This leaves little flexibility in terms of access to services, and tricky patching if the ceiling ever needs to be altered. This type of ceiling is not ideal where access to services above is required.
Fire safety
Paint on a concrete soffit is considered a non-combustible finish as the thickness of the paint is usually less than
0.5 mm – refer to manufacturers’ specifications, and consult with the SANS Part T (4.13).
Indoor air quality: Humidity
Generally, paints are not adversely affected by a reasonable amount of moisture being generated by the presence of taps or wet fittings in a room. Enamel paints are most resistant to absorbing moisture, when compared to PVA-type paints.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
Paints are notorious for high VOC emissions, although manufacturers are now working on products with reduced or zero VOCs. Refer to product specific literature.
Acoustics
The hard surface of painted soffits reflects sounds and where acoustics are important, there are certainly better options available.
Aesthetics
While paint can be used effectively to introduce colour for features or emphasis, generally on ceilings in areas where infection prevention is important, the ceilings should be kept single colours - white or light colours – this ceiling would be used in areas where aesthetics is not the highest priority.
Cementitious board – nail-up ceilings
General description and properties
Plain and textured ceiling boards are available for nail-up applications where joints are not a problem. These boards are manufactured from a combination of cement, silica and organic fibres. They are available in 4 and 6 mm thicknesses, and can be nailed at regular intervals to the overhead structure.
The joints between the ceiling boards can be finished using joiners or cover-strips. The ceiling boards can also be fixed between exposed beams.
Although no paint finish is required, paint can be applied. (Refer to comments on paint on plaster above.)

Infection prevention
The textured boards and the joining strips will create areas where microbes can grow. This ceiling finish is therefore not suitable for areas where infection prevention is critical.
Cleaning and maintenance
Nail-up cementitious boards are unaffected by moisture and resistant to corrosion. When painted they are easy to clean and stain-resistant. They are relatively lightweight (compared to a concrete soffit), low maintenance and durable. Replacement is possible if boards do get damaged, but this would be disruptive to the functioning of the room.
Access to services
Access panels need to be planned in the structure prior to painting. This leaves little flexibility in terms of access to services, and tricky patching if the ceiling ever needs to be altered. This type of ceiling is not ideal where access to services above is required.
Fire safety
Nail-up cementitious boards are non-combustible.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
These painted boards are well-suited to areas of high humidity as they are not affected by moisture.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
These boards can be supplied with thermal insulation backing, which will reduce the heat load on the building from roof spaces where applicable. Fibres are safe and recyclable, and manufacturers claim low embodied energy used for assembly and construction. Refer to product specific literature. Emissions from paints should be considered.
Aesthetics
This type of ceiling board is aesthetically acceptable, and with paint, can be used to create an interesting functional ceiling.
Acoustics
The hard surface reflects sound and will not aid in sound absorption in the room it covers.
Vinyl-clad ceiling tiles in suspended grid
General description and properties
Vinyl-clad ceiling tiles are manufactured from cement, silica and organic fibres. They are available in 4 and 6 mm thicknesses and are clad on the exposed surface with vinyl. They are suitable for 1 200 x 600mm or 600 x 600mm exposed ceiling grids. The grids are suspended from the structure above. The ceiling tiles can also be supplied with 25 mm insulation backing. No further painting or finishing is required.
Infection prevention
The vinyl finish is impervious, and vinyl inhibits the growth of bacteria. The boards are unaffected by moisture, and can be washed regularly. This makes them suitable for infection prevention. There are however joints, so the ceiling is not seamless.
Cleaning and maintenance
As mentioned, the vinyl-clad tiles are unaffected by moisture and resistant to corrosion. They are easy to clean and stain-resistant. They are relatively lightweight (compared to a concrete soffit), low maintenance and durable. Replacement is very easy if boards do get damaged, with very little disruption to the room function.
Access to services
Access panels are easily allocated in a suspended grid ceiling, and the removable tiles allow for maximum flexibility for access to services in the ceiling void.
Fire safety
Vinyl-clad boards are non-combustible; however, fire load of the ceiling grid should be ratified with the manufacturer.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
These boards are well-suited to areas of high humidity as they are not affected by moisture.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
These boards can be supplied with thermal insulation backing, which will reduce the heat load on the room. Fibres are safe and recyclable, (no asbestos fibres) and manufacturers claim low embodied energy used for assembly and construction. However, the vinyl has low VOC emissions, when compared to some paints. Refer to product specific literature.
Aesthetics
This type of ceiling board gives a hygienic impression and is aesthetically acceptable. Tiles can also be printed with designs where budgets allow.
Acoustics
The surface is relatively hard, and does not assist with acoustic control or absorb sounds.

Acoustic ceiling tiles in suspended grid
General description and properties
These mineral fibre acoustic ceiling tiles – nominally 20 mm thick - have a pre-painted textured and perforated finish. The boards can be supplied with various edge finishes suitable for an exposed grid, or recessed grid with regular or chamfered edges. They are suitable for 1200 x 600mm or 600 x 600mm ceiling grids. The grids are suspended from the structure above. No further painting or finishing is required.
Infection prevention
The fissured surface may harbour dust and bacteria, making this type of ceiling board unsuitable for areas where infection prevention is critical – such as theatres. Some manufacturers do produce an ‘anti-microbial’ tile. Refer to the section on Selection Criteria- Infection Prevention for more discussion on this aspect. The boards cannot be washed as they will absorb moisture. Dirty or stained panels can be replaced easily. There are also joints, so the ceiling is not seamless.
Cleaning and maintenance
Since the boards are adversely affected by moisture, they can only be brush-cleaned and must be kept dry. Dirt often gathers where air-conditioning ducts blow across these tiles, and these then are difficult to clean. They are lightweight and fairly low maintenance. Replacement is very easy if boards do get damaged, with very little disruption to the room function, although batch colours and textures may vary.
Access to services
Access panels are easily allocated in a suspended grid ceiling, and the removable tiles allow for maximum flexibility for access to services in the ceiling void.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
These boards are unsuited to areas of high humidity as they absorb moisture and will swell and droop over time when exposed to moist conditions.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
These boards provide some thermal insulation which will reduces the heat load of the building. The tiles do have low VOC emissions which will vary according to the manufacturer. Refer to product specific literature.
Aesthetics
The patterns of the fissures on this type of ceiling tile can create an interesting ceiling which is aesthetically acceptable.
Acoustics
The perforated surface is excellent for sound absorption and this product is well-suited to areas where noise reduction is prioritised.

Pressed metal ceiling tiles in suspended grid
General description and properties
Pressed metal tiles are manufactured from galvanised steel, and are then epoxy-coated for a durable finish. The ceiling tiles are made to a variety of sizes. Stainless steel tiles are also available. Perforations are made in the surface – in different patterns and diameter to reduce the weight and improve acoustic performance. They are laid in a suspended ceiling grid, or can be hinged to the grid to open downwards. No further painting or finishing is required.
Infection prevention
The perforated surface may harbour dust and bacteria, and the joints mean the ceiling is not seamless. This type of ceiling is not suitable for areas where infection prevention is critical. The tiles are however washable.
Access to services
The hinged access tiles are purpose-made for access to services in the ceiling void as they are hinged to swing down leaving the void clear of grid transoms. The lay-in type of panel is also removable in a suspended grid ceiling, allowing for maximum flexibility for access to services in the ceiling void.
Cleaning and maintenance
The epoxy-coated tiles are unaffected by moisture and resistant to corrosion. They are easy to clean and stainresistant. They are robust and unlikely to be damaged easily, making them very low maintenance and durable. Replacement is easy if tiles do need replacing, with very little disruption to the room function.
Fire safety
Metal is listed as non-combustible in the SANS Part T as tested under 10177-5, however fire load of the ceiling grid should be ratified with the manufacturer.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
These boards are unaffected by humidity and are suitable for use in humid, moist conditions.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
The metal tiles are generally made from recycled material and can also be recycled. Refer to product specific literature. The tile itself does not provide any insulation value.
Aesthetics
The patterns of the perforations create an interesting effect which is aesthetically-pleasing, and used together with bulkheads for lighting creates an interesting ceiling.
Acoustics
The perforated surface contributes to sound absorption and compensates somewhat for the hard, reflective metal surface.

Rigid extruded polystyrene panels (XPS)
General description and properties
Polystyrene ceiling panels combine the aesthetic of a ceiling panel with the insulation properties of closed-cell insulation board. These panels are manufactured from high-density rigid extruded polystyrene. These can be supplied smooth for a flush appearance, bevelled to pronounce the 600 mm joint, or grooved at 100 mm intervals to resemble tongue and groove timber planks. Although neatly finished, painting with PVA is recommended. The boards can be fitted over-purlin, nailed-up to brandering, or between exposed trusses, and should be ordered in long lengths to avoid butt-joints on ends. The panels are available in thicknesses of 25, 30 or 40 mm.
Infection prevention
The rigid polystyrene neither absorbs moisture, nor is it affected by moisture. This prevents the growth of mould or bacteria on the product, and the polystyrene itself is not a nutrient source for bacteria. However, if substantial soiling/dust is allowed to build-up on the surface, the soiling could provide reservoirs for bacterial growth - as with any product. In certified tests, (by SANAS accredited laboratory) the rigid polystyrene showed no microbial growth and was declared suitable for use in the food industry. Since the surface is jointed, however, its use will be limited.
Access to services
Access panels need to be planned in the ceiling prior to installation. This leaves little flexibility in terms of access to services, and patching is difficult if the service access ever needs to be altered. This type of ceiling is not ideal where access to services above the ceiling is required.
Cleaning and maintenance
The panels are unaffected by moisture, resistant to corrosion and easy to clean. They can however be mechanically damaged, and should preferably be fitted at high levels. Replacement of damaged panels would create a fair amount of disruption.
Fire safety
Although polystyrene is combustible, it has no flame-spread characteristics, and will not add to a fire load. It is classified as B/B1/2/HV S and USP in terms of SANS 428/SANS 10177, which means that it is combustible (B), but has no flame-spread (B1), can be used where combustible materials are permitted in various building types (Class 2 of occupancy) and it can be used in horizontal and vertical applications (H and V) with or without sprinklers. Note that ’healthcare’ falls into Class 2 of occupancy, but ‘hospital’ falls into Class 1 – noncombustible materials only.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
These boards are unaffected by humidity and are suitable for use in humid, moist conditions.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
The insulation properties of the rigid polystyrene will reduce the heat load and act as a bulk insulator. The Rvalues increase with the thickness from 0.833 (for 25 mm thick board) to 2.667 for 80 mm thickness – double layer). Rigid polystyrene panels have no obvious odour, but under high heat conditions (near heat-generating light fitting , for example), some aromatic hydrocarbons are released. The manufacture of rigid polystyrene panels requires the use of HCFC-gasses, however, the measure of these gasses is at levels less than 150 ppm even where large quantities are stored. The VOC emissions of adhesives used to install the product should also be considered.
Aesthetics
The tongue and groove pattern creates interest in the surface of the ceiling, and can evoke a homely residential feel to the room/area. This can be used to good effect in healthcare facilities.
Acoustics
The rigid polystyrene boards do not absorb sound and should not be used for acoustically-sensitive areas.

Expanded polystyrene panels (EPS)
General description and properties
These laminated expanded polystyrene panels are made up of low-density fire-retardant board finished with a fire retardant PVC-foil, the surface of which can be embossed or smooth. The layers are bonded under high temperatures. The panels can be supplied full size in 4.8 x1.2 m boards for over-purlin fixing, or cut to suit a suspended ceiling grid (1 200 x 600mm). It can also be installed under purlin or between rafters. PVC H-joiners are used at junctions. Because the panels are very light, wire-hung suspended grids are not recommended, as these could result in drafts lifting the ceiling. Rigid steel battens are required. No further painting or finishing is required. The panels are generally available in 40 mm thickness.
Infection prevention
The rigid polystyrene neither absorbs moisture, nor is it affected by moisture. This prevents the growth of mould or bacteria on the product, and the PVC-foil surface finish is not a nutrient source for bacteria. However, if substantial soiling/dust is allowed to build-up on the surface, the soiling could provide reservoirs for bacterial growth - as with any product. Since the surface is jointed, however, its use will be limited to areas where ‘seamless’ ceiling surfaces are not required.
Access to services
Access panels are easily accommodated where the suspended grid system is utilised. Where nail-up systems are installed, access panels need to be planned in the ceiling prior to installation.
Cleaning and maintenance
The panels are unaffected by moisture, resistant to corrosion and easy to clean. They do not require repainting or maintenance apart from occasional cleaning. Replacement of damaged panels in the suspended grid is not disruptive.
Fire safety
Although polystyrene is combustible, it has no flame-spread characteristics, and will not add to a fire load. It is classified as B/B1/2/HV S and USP in terms of SANS 428/SANS 10177, which means that it is combustible (B), but has no flame-spread (B1), can be used where combustible materials are permitted in various building types (Class 2 of occupancy) and it can be used in horizontal and vertical applications (H and V) with or without sprinklers. Note that ‘healthcare’ falls into Class 2 of occupancy, but ‘hospital’ falls into Class 1 - noncombustible materials only. Fire-rating of the suspended grid should also be considered.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
These boards are unaffected by humidity and are suitable for use in humid, moist conditions.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
The excellent insulation properties of the polystyrene will reduce the heat load and act as a bulk insulator. The manufacture of expanded polystyrene panel does not require the use of CFCs and no adhesives are used to install the product.
Aesthetics
The wood-grain or random textured embossing creates interest in the surface of the ceiling. The board has a slightly shiny finish.
Acoustics
The rigid polystyrene boards do not absorb sound and should not be used for acoustically-sensitive areas.
Timber and timber composites
General description and properties
Timber products have been used in ceilings for many generations. The most common locally available timber is maranti and pine - in various standards and quality. The versatility of the timber products provides almost unlimited options in terms of fitting ceilings - from standard tongue and groove planks, to slatted battens. The timber is usually varnished or treated with a preservative. Engineered timber products are also available with melamine or veneer finishes.
Infection prevention
Timber is a source of nutrient to bacteria, and good maintenance and cleaning will be needed to ensure that mould and other bacteria are prevented from establishing. Timber would not be suitable for areas where a seamless finish is required due to the jointing. Acrylic resin-based antibacterial varnish containing silver has superior microbial and chemical resistance, and will extend the life span of the timber. Medium-density fibreboards (MDFs) with melamine/veneer finishes could be installed in suspended grids.
Access to services
Access panels in a timber ceiling would need to be planned before the installation, and a purpose-made hinged or removable door created. This leaves little flexibility in terms of access to services, and patching is difficult if the service access ever needs to be altered. This type of ceiling is not ideal where access to services above the ceiling is required. Where suspended grids are installed, this provides easy access to services.
Cleaning and maintenance
The timber slats or planks are washable, but access to narrow grooves may limit the effectiveness of cleaning. Occasional re-varnishing would be required, which could be disruptive to the activities in such areas. Engineered MDF ceiling panels do not require repainting and should not be put in contact with water, but cleaned by dry brushing/vacuuming. These panels can easily be replaced however, where installed in a suspended grid.
Fire safety
In terms of SANS 10400, timber is combustible and not permitted for use in ceilings for the Occupancy E2 (hospitals). It is however permitted under certain conditions for E3 and E4 occupancies.
Indoor air quality: Humidity
Well-varnished timber will be protected from the effects of moisture, but generally, timber should not be used in rooms where humid, moist conditions persist. MDF ceiling panels are not suitable for humid or wet areas.
Indoor air quality: Emissions and insulation
Timber is a natural product that does not emit VOCs. However, engineered timber products such as mediumdensity fibre-board contains a higher resin to wood ratio than any other urea-formaldehyde pressed wood product, and is recognized as being the highest formaldehyde emitting pressed wood product. (source: US Environmental Protection Agency). These VOCs are fairly quickly dissipated. Refer to product specific literature. The timber planks or engineered panels do not provide much insulation value.
Aesthetics
The patterns of the perforations create an interesting effect which is aesthetically pleasing, and used together with bulkheads for lighting creates an interesting ceiling.
Acoustics
The perforated surface of the slatted ceiling or MDF tiles aid in reducing the re-transmission of sound. MDF acoustic tiles are specifically manufactured for their superior performance in absorbing sound.

Performance
Performance categories
The properties described in the selection criteria in Section C above have been listed in the table below, and then grouped into five performance categories that would satisfy the requirements in various areas within a healthcare facility
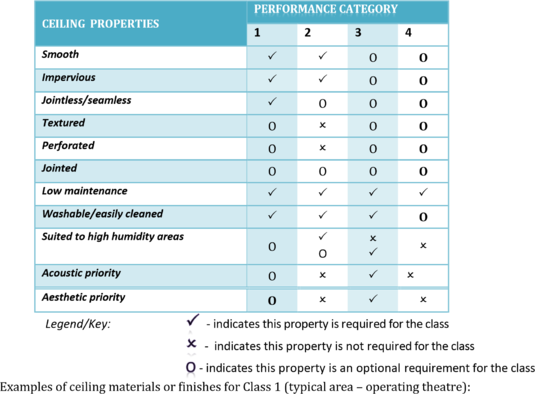
- Skimmed or plastered and painted – seamless ceiling
Examples of ceiling materials or finishes for Class 2 (typical room – general ward):
- Vinyl-clad or pressed metal tiles in grid, etc.
Examples of ceiling materials or finishes for Class 3 (typical area – dirty utility):
- Skimmed or plastered and painted – jointed, vinyl-clad or pressed metal tiles in grid; expanded or extruded polystyrene panels, etc.
Examples of ceiling materials or finishes for Class 4 (typical area – office or waiting room):
- Acoustic ceiling tiles in grid; timber and composite panels, etc.
Examples of ceiling materials or finishes for Class 5 (typical area – plant room):
- Expanded or extruded polystyrene; skimmed or plastered and painted – jointed; vinyl-clad or pressed metal tiles in grid; expanded or extruded polystyrene panels, etc.
Refer to Table 2 – Matrix of recommended performance categories to establish what performance category the ceiling of the room in question will require – this could be a number of options in some cases.
Performance categories recommended per room
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 | 5 | |||||
| Acute In-patient Wards (Adults) | Circulation Space | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | * | |||
| Day Lounge (patients) | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility Room (Sluice) | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | * | * | |||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| General Ward (single or multi-bed) | * | |||||
| Isolation Ward | * | |||||
| Kit Room | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Patient ablutions | * | |||||
| Patient-assisted Ablution | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | * | ||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Waiting area (public) | * | |||||
| Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Ward Nurse Station | * | |||||
| Administration Department | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Offices/Interview Rooms | * | * | * | |||
| Reception | * | |||||
| Boardroom | * | |||||
| Stores | * | |||||
| Kitchenette | * | |||||
| Records Room | * | |||||
| Print room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Waiting Area (public) | * | |||||
| Casualty and Trauma | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | * | |||
| Dirty Utility Room (Sluice) | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | * | * | |||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Hazmat Shower | * | |||||
| Minor Theatre/Suture Room | * | |||||
| Observation Area | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 5 | ||||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Patient-assisted Ablution | * | |||||
| POPS Suite | * | |||||
| Public WCs | * | |||||
| Reception/Nurse Station | * | |||||
| Rehydration Area | * | |||||
| Resuscitation Area | * | |||||
| Scrub area | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions and Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Waiting Area (public) | * | |||||
| Central Sterilising and Supply Department (CSSD) | Dirty Utility | * | ||||
| Chemical Store | * | |||||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Linen | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Packing | * | |||||
| Plant Room | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | * | ||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Sterile Storage | * | |||||
| Sterilisation (autoclaves) | * | |||||
| Trolley Wash | * | |||||
| Washing and Disinfecting Area | * | |||||
| Community Health Centre | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | ||||
| Delivery Room | * | |||||
| Dental Surgery | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility Room (Sluice) | * | |||||
| Dispensary | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Guard House or Security Kiosk | * | |||||
| Isolation/Separate Nursing Ward | * | |||||
| Linen Store | * | |||||
| Observation Area | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | ||||
| Offloading or Holding Area for Pharmacy | * | |||||
| PABX/Server Rooms | * | |||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Patient-Assisted Ablution | * | |||||
| Pharmacy | * | |||||
| Plant Room | * | |||||
| POPS Suite | * | |||||
| Public WCs and Change Rooms | * | |||||
| Reception/Nurses’ Station | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 5 | ||||||
| Records Room | * | |||||
| Recovery Area | * | |||||
| Rehydration Area | * | |||||
| Resuscitation Area | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Trolley Bay (entrances) | * | |||||
| Ultrasound Room | * | |||||
| Ward | * | |||||
| Waiting Area (public) | * | |||||
| X-Ray Room | * | |||||
| Day Clinic (Department) | Circulation Space | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | * | |||
| Dirty Utility Room (Sluice) | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| General Ward (single or multi-bed) | * | |||||
| Kit Room | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Operating Theatre | * | |||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Patient Waiting | * | |||||
| Recovery Area | * | |||||
| Scrub Area | * | |||||
| Setting Area | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions and Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Waiting Area (public) | * | |||||
| Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Ward Nurses’ Station | * | |||||
| High Care or Cardiac Care Unit (HC/CCU) | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | * | * | |||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Isolation Ward | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Nurses’ Station | * | * | ||||
| Open Ward Area | * | |||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 | 5 | |||||
| Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Intensive Care Unit (ICU) | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | * | * | |||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Isolation Ward | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Nurses’ Station | * | * | ||||
| Open Ward Area | * | |||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Kitchen – (Main Hospital) | Bulk Dry Goods Store | * | ||||
| Chemical Store | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Cold Room/Freezer | specialised | |||||
| Cooking Area | * | |||||
| Cutlery/Crockery Store | * | |||||
| Dishwashing and Potwashing Area | * | |||||
| Food Preparation Area | * | |||||
| Office | * | |||||
| Plating/Serving Area | * | |||||
| Receiving Area | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | * | ||||
| Trolley Wash Area | * | |||||
| Laboratory
(Pathology/Cytology/Haemato logy/Chemistry) (Biosafety Level 2)
|
Blood and Blood Products Store | * | ||||
| Cell and Tissue Laboratory | * | |||||
| Cytopathology Sample Storage | * | |||||
| Clinical Material Store | * | |||||
| Disposal Area (dangerous materials) | * | |||||
| Drug and Vaccines Store | * | |||||
| Flammable Goods Store (external) | * | |||||
| Gas Cylinder and Pressure Vessel Store | * | |||||
| Hazardous Substances Store | * | |||||
| Histopathology Laboratory | * | |||||
| Microbiology Laboratory | * | |||||
| Offices | * | * | * | |||
| POCT consulting room | * | |||||
| Reagents/Chemical Stores | * | |||||
| Records Rooms | * | |||||
| Sample Collection Laboratory | * | |||||
| Specimen Reception and Sorting Rooms | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 | 5 | |||||
| Stores (protective clothing/equipment) | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room (including lockers) | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Laundry – (Main Hospital) | Assembly, Packing and Dispatch | * | ||||
| Chemical Store | * | * | ||||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Pressing | * | |||||
| Sorting | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Stores | * | |||||
| Washing Room | * | |||||
| Maternity/Delivery Department | Baby Bathing Area | * | ||||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Delivery Suite | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility Room | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| First Stage Room | * | |||||
| Kit Room | * | |||||
| Linen Store | * | |||||
| Milk Kitchen | * | |||||
| Nurse Station | * | |||||
| Nursery | * | |||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Viewing Area | * | |||||
| Waiting Area | * | |||||
| Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Wards | * | |||||
| Mental Health Facility | Body Room | * | ||||
| Children's Play Area | * | |||||
| Clean Utility | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room/Station | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | * | |||
| Counselling Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Linen | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility (Sluice) | * | |||||
| ECT Procedure Room | * | |||||
| En Suite Bath/Shower Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Group Therapy Room | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 5 | ||||||
| Gymnasium (OT and physio) | * | |||||
| IT Room | * | |||||
| Kit Room | * | |||||
| Linen Store | * | |||||
| Medicine Store | * | |||||
| Multi-Purpose Hall | * | |||||
| Nurses’ Station | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Patient-Assisted Bathroom/Shower | * | |||||
| Patient Dining Room | * | |||||
| Patient Laundry | * | |||||
| Patient Lounge | * | |||||
| Pharmacy | * | |||||
| Quiet Room | * | |||||
| Records Room | * | |||||
| Seclusion Room | * | |||||
| Security Control Room | * | |||||
| Security Search Room | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room and WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Wards | * | |||||
| Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Waste Disposal Room | * | |||||
| Mortuary | Blue Room | * | ||||
| Circulation Space | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility | * | |||||
| Instruments Room | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Medical Observation Room | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Pathologist Change Room | * | |||||
| Post-Mortem Room | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Viewing Room | * | |||||
| Visitors’ Waiting Room | * | |||||
| Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
(NICU) |
Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Incubator Ward Area | * | |||||
| Isolation Ward | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Milk Kitchen | * | |||||
| Mothers’ Rest Area | * | |||||
| Nurses’ Station | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 5 | ||||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Operating Theatre (Department) | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Nurses’ Station | * | |||||
| Operating Theatre | * | |||||
| Post-Operative Recovery Area | * | |||||
| Pre-Operative Holding Area | * | |||||
| Scrub-up Area/Room | * | |||||
| Setting Room | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Outpatients Department | Reception/Nurses’ Station | * | ||||
| Admissions Room | * | * | * | |||
| Baby Changing Area | * | |||||
| Children’s Play/Waiting Area | * | |||||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | ||||
| Dirty Utility Room | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Kitchenette | * | |||||
| Linen Store | * | |||||
| Offices | * | * | * | |||
| POPS Room | * | |||||
| Public Ablutions | * | |||||
| Records Room | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Waiting Areas (public) | * | |||||
| Wheelchair Storage Area | * | |||||
| Paediatric Ward | Child-Assist Ablution | * | ||||
| Circulation Space | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | * | |||
| Dirty Utility (isolation) | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility Room (Sluice) | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| General Ward (single or multi-bed) | * | |||||
| Isolation Ward | * | |||||
| Kit Room | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 | 5 | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Milk/Ward Kitchen | * | |||||
| Nurses’ Station | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Parent Ablutions | * | |||||
| Play Area (patients) | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Pharmacy/Dispensary | Cleaners’ Room | * | ||||
| Bulk Stores | * | |||||
| Circulation Space | * | |||||
| Counselling Cubicle | * | |||||
| Dispensary | * | |||||
| Liquid Filling Room | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Offloading Bay | * | |||||
| Patient Waiting Room | * | |||||
| Schedule Drugs Strong Room | * | |||||
| Staff Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Tablet Packing Room | * | |||||
| Vacolitre Stores | * | |||||
| Physiotherapy Department | Audiology Testing | * | ||||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | * | * | |||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Gymnasium | * | |||||
| Kitchenette | * | |||||
| Occupational Therapy Room | * | |||||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Reception | * | |||||
| Speech Therapy | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Waiting Area | * | |||||
| Primary Health Clinic | Circulation | * | ||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| Consulting Room | * | |||||
| Delivery Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility Room (Sluice) | * | |||||
| Dispensary and Pharmacy | * | |||||
| Duty Room | * | |||||
| Equipment Store | * | |||||
| Guard House or Security Kiosk | * | |||||
| Linen Store | * | |||||
| Observation/Rehydration Area | * | |||||
| Department | Room Name | Ceiling Performance | ||||
| 1 2 3 4 | 5 | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Public Ablutions | * | |||||
| Plant Room | * | |||||
| POPS Suite | * | |||||
| Reception/Nurse Station | * | |||||
| Records Room | * | |||||
| Staff Ablutions and Change Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Surgical Sundries Store | * | |||||
| Treatment Room | * | |||||
| Trolley Bay (entrances) | * | |||||
| Waiting Area (public) | * | |||||
| Radiology (Diagnostic) | Bucky Room (general X-ray Room) | * | ||||
| Change Cubicles | * | |||||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Cleaners’ Room | * | |||||
| CT/MRI Scan Room | * | |||||
| Dirty Utility/Sluice | * | |||||
| Fluoroscopy Room | * | |||||
| Fluoroscopy Control Room | * | |||||
| Inpatient Waiting Area | * | |||||
| Kitchenette | * | |||||
| Linen Room | * | |||||
| Mammogram Room | * | |||||
| Office | * | * | * | |||
| Patient Ablutions | * | |||||
| Public Waiting Area | * | * | ||||
| Porters and Wheelchair/Trolley Parking | * | * | ||||
| Reception | * | |||||
| Records Room | * | |||||
| Server Room | * | |||||
| Staff Rest Room | * | |||||
| Staff WCs | * | |||||
| Stores (Equipment/General) | * | |||||
| Ultrasound Room | * | |||||
| Telemedicine Room | * | |||||
| Viewing Room/CR Room/Reporting Area | * | |||||
| Residences (e.g., Nurses) | Ablutions | * | ||||
| Bedrooms | * | * | * | * | ||
| Circulation | * | |||||
| Kitchenette | * | |||||
| Lounge | * | |||||
| Offices | * | |||||
| Public Ablutions | * | |||||
| Reception | * | |||||
| Stores | * | |||||
| Waiting Areas (public) | * | |||||
Definitions
Terminology
Aggregation Collected together from different sources and considered a whole.
Ambulant/ambulatory (of a patient) Being able to walk or move around; not being confined to a bed.
Bacteriostatic A word used to describe the property of a material which claims to inhibit the multiplication of bacteria.
Bariatric Describing the condition of obesity.
Bonded Chemically attached or fused in layers.
Guarantee A document setting out a promise of quality made by a manufacturer or the provider of a service, a formal promise that a product will be repaired free of charge if it breaks or fails within a particular period or that substandard work will be redone.
Homogenous Consisting of things of similar type throughout.
Heterogeneous Consisting of various layers or types throughout.
Hygroscopic Readily absorbing moisture from the atmosphere.
Hydrophobic Water-repellent.
Impervious Not allowing passage through (usually of water/moisture).
Interstices Small holes or perforations.
Jointed Junctions which may be open or covered, but not completely sealed and smooth.
Jointless Without joints or having joints, which are sealed by materials and methods which make the whole surface imperious and prevent the collection of dirt and bacteria in the joint.
Olfactory Relating to the smell or the sense of smell.
Perfusion Inject liquid into tissue or organ by circulating through blood vessels in the body.
Polyamide A synthetic polymer made by the linkage of an amino group of one molecule and a carboxylic acid group of another, including many synthetic fibres such as nylon.
Resilient finish The quality of a material to spring back quickly into shape after being bent, stretched, or squashed, resilient flooring refers to flooring materials which have a relatively firm surface, yet characteristically have ‘give’ and ‘bounce back’ to their original surface profile from the weight of objects that compress its surface.
Seamless A surface without open joints or junctions, or where such joints are completely sealed and smooth to create a continuous and whole membrane.
Slip-resistant A quality of a finish to prevent wet or dry slipping. This relates to the friction of the material in relation to the pedestrian traffic across it, and also the type of footwear users have when walking across this finish. Wet pendulum and dry floor friction tests indicate comparative results. Refer to section B4.3.3 for more detail.
Smooth surface A flat surface without projections, indentations or perforations such as a brush-painted plastered surface.
Textured A surface finish which is not smooth, but has a fissured/embossed or ridged finish.
Tufted A group of threads drawn through a fabric and tied securely beneath the surface.
Vitrified To change a material into glass, under high heat and other conditions.
Washable A term implying that a finish can be repeatedly and regularly cleaned using water and water-diluted cleaners without detrimental effect to the finish.
Warranty A written promise to repair or replace a product that has a manufacturing fault. This commonly comes with conditions and is limited to a timeframe given at the time of purchase.
Abbreviations
| CFC | Chlorofluorocarbon |
| CHD | Centre for Health Design |
| ENT | Ear, nose and throat |
| HAI | Healthcare-associated infections |
| HCFC | Hydrochlorofluorocarbon |
| HDF | High-density fibreboard |
| IEQ | Indoor Environmental Quality |
| IUSS | Infrastructure Unit Systems Support |
| MDF | Medium-density fibreboard |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, (which is a common skin bacterium that is resistant to a range of antibiotics), otherwise referred to as multi-drug resistant bacteria |
| NDoH | National Department of Health |
| OoM | Order of Magnitude |
| PMIS | Project Management Information System |
| PMSU | Project Management Support Unit |
| PuR | Polyurethane-resistant |
| PVC | Polyvinylchloride |
| RC | Recommendation Committee |
| VOC | Volatile organic compound |
References
Bibliography
Alcorn, A. and Wood, P., 1998. New Zealand building materials embodied energy coefficients database. (Volume II-Coefficients). Wellington, New Zealand: Centre for Building Performance Research.
AASA, the School Suprintendents Association, 2009. Improving indoor air quality: Materials selection. [online] Alexandria, Egypt: AASA. Available at: http://www.aasa.org/search.aspx?query=Materials+Selection+[Accessed 9 April 2014].
Cement & Concrete Institute (CCI), 2009. Sand-cement screeds and concrete toppings for floors. [pdf] Midrand, South Africa: CCI. Available at:
http://www.afrisam.co.za/media/13770/Sand_cement_floor_screeds_and_concrete_toppings_for_floors.pdf[Ac cessed 9 April 2014].
Center for Health Assets Australasia, 2009. Floor coverings in healthcare buildings. (Technical series TS-7 version 1.1). New South Wales:NSW Health.
Dean, Y., 1996. Finishes. 4th ed. Harlow, UK: Addison Wesley Longman Ltd.
Department of Health (DH), 2010. Core elements: Health Building Note 00-03: Clinical and clinical support spaces. UK: DH.
Department of Health (DoH), 1980. Regulations governing private hospitals and unattached operating theatres. (Government notice No. R.158 of the Health Act, 1971. (C.63). Cape Town South Africa: Government Gazette.
Department of Health Finance and Investment Directorate Estates and Facilities Division, 2006. Health
Technical Memorandum 61: Building component series flooring. [pdf] London: The Stationery Office. Available at: http://www.wales.nhs.uk/sites3/Documents/254/HTM%2061%202006.pdf [Accessed 9 April 2014].
Department of Health Gateway Review, Estates & Facilities Division, 2011. Performance requirements for building elements used in healthcare facilities. (Version:0.6:England). [pdf] Leeds: HMSO. Available at: http://www.derbyshirelmc.org.uk/Guidance/8941-England-8941_0.6_England.pdf [Accessed 9 April 2014].
Department of Health, n.d. R&D project B(04)02: Developing an integrated system for the optimal selection of hospital finishes. Aberdeen, Scotland: Department of Health.
HermanMiller Healthcare, 2006. Sound practices: Noise control in the healthcare environment. (Research summary/2006). Zeeland, Michigan: Herman Miller.
Joseph, A., Malone, E., Pati, D. and Quan, X., 2011. Healthcare environmental terms and outcome measures: An evidence-based design glossary. Concord, CA:The Center for Health Design.
Jung, W.K., Koo, H.C., Kim, K.W., Shin, S., Kim, S.H. and Park, Y.H., 2008. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(7), pp.2171-2178.
Lavy, S., 2010. Facility managers’ preferred interior wall finishes in acute-care hospital buildings. In: CIB, 18th CIB World Building Congress: Facilities management and maintenance. Salford, United Kingdom, 10-13 May 2010. Salford, United Kingdom: CIB.
Makison, C. and Swan, J., 2005. The effect of humidity on the survival of MRSA on hard surfaces. (R&D report B(03)02). [pdf] London: Estates and Facilities Division of the Department of Health. Available at: http://www.wales.nhs.uk/sites3/Documents/254/B(03)02%20MRSA.pdf [Accessed 9 April 2014].
Nanda, U., Malone, E. and Joseph, A., 2012. Achieving EBD goals through flooring selection & design. [pdf] Concord, CA:The Center for Health Design. Available at:
http://www.healthdesign.org/sites/default/files/chd_achieving_ebd_goals_through_flooring__design_final_0.pd f [Accessed 9 April 2014].
NHS Estates, 2005. Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 56: Building component series: Partitions. UK: TSO.
NHS Estates, 2005. Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 60: Ceilings. 2nd ed. UK: TSO.
NHS, National Services Scotland, 2006. Scottish Health Technical Memorandum (SHTM) 61: Building component series: Flooring. Scotland:Health Facilities Scotland.
NHS, National Services Scotland, 2007. Scottish Health Facilities Note 30: Infection control in the built environment: Design and planning. (Version 3). Scotland:Health Facilities Scotland.
NHS, National Services Scotland, 2009. Scottish Health Technical Memorandum (SHTM) 61: Building component series: Flooring. Scotland:Health Facilities Scotland.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP (PwC) in association with the University of Sheffield and Queen Margaret University College, 2004. The role of hospital design in the recruitment, retention and performance of NHS nurses in England. (Full report). [pdf] Edinburgh: Commission for Architecture and the Built Environment (CABE). Available at: http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110118095356/http:/www.cabe.org.uk/files/therole-of-hospital-design.pdf [Accessed 9 April 2014].
Welsh Health Estates, 2009. Health Building Note 04-01: Adult in-patient accommodation. Cardiff, Wales:Welsh Health Estates.
Wolkoff, P., 1999. How to measure and evaluate volatile organic compound emissions from building products. A perspective. The Science of the Total Environment, 227(1999), pp.197-213
Websites: Further reading
https://www.transparency.perkinswill.com
http://www.gatech.edu
http://www.GreenhealthMagazine.org http://greenhomeguide.com
http://gbcsa.org.za
http://www.green-buildings.com
http://www.healthcaredesignmagazine.com
http://www.isoboard.com
http://www.isolite.co.za
http://www.everite.co.za
http://www.armstrong.com
http://www.owa.co.za
Photographic and illustration credits
Cover photo: M. Swinney
| Fig.1 | M. Swinney |
| Fig.2 to 5 | Diagram by C. Hiralal |
| Fig.6 | R.Cubbin based on Lifecycle Floor Cost Table – by Nora®, USA |
| Fig.7 | G. Abbott- CSIR |
| Fig.8 | R.Cubbin |
| Fig.9 | M. Swinney |
| Fig.10 | R. van Rensburg |
| Fig.11 | M. Swinney |
| Fig.12 | R. van Rensburg |
| Fig.13 to20 | M. Swinney |
| Fig.21 | R. van Rensburg |
| Fig.22 | M. Swinney |
| Fig.23 | R. Cubbin |
| Fig.24 | M. Swinney |
| Fig.25 | R. Cubbin |
| Fig.26 to28 | M. Swinney |
Please help to expand this page. |